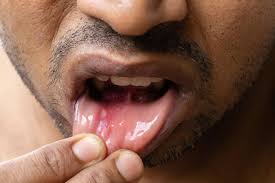
TREATMENT OF MOUTH ULCERS
Treatment of mouth ulcers. Small sores known as mouth ulcers can develop on the roof of your mouth, inner cheeks, lips, tongue, or gums. They can be caused by a wide range of factors, such as mental stress, hormone changes, and minor accidents. A lot of oral ulcers heal themselves. Others could need medical attention.
TREATMENT OF MOUTH ULCERS
Any sore that develops inside your mouth is called a mouth ulcer. You may have one or more of these sores, which are often red, yellow, or white. Canker sores and the sores brought on by hand, foot, and mouth disease are two types of mouth ulcers, which are painful, usually small lesions that form in your mouth or at the base of your gums and can make eating, drinking, and speaking uncomfortable.
Types
There are numerous varieties of mouth lesions and sores, such as:
1. Canker sores
also known as aphthous ulcers. The most prevalent kind of mouth ulcers are these. The actual etiology of these conditions and the reasons why some persons are more susceptible to them than others remain unknown to medical professionals. Acidic meals, stress, and even small trauma (such as biting your cheek) are causes. Typically, canker sores are yellow or white with red rims.
2. Lichen planus in the mouth
White, lace-like lesions inside your mouth and itchy rashes are symptoms of this illness. Females 50 years of age or older are most frequently affected by oral lichen planus, which is an immune system reaction.
3. Thrush in the mouth
Inside your mouth, this fungal infection is caused by an overabundance of yeast known as Candida albicans. It frequently occurs after taking antibiotics or when your immune system isn’t functioning at its best. Mouth sores and patches that are red and creamy white are caused by oral thrush.
4. Cancer of the mouth
Red or white mouth sores or ulcers are symptoms of oral cancer lesions. These sores are not going to go away on their own. Inform your healthcare physician if, after three weeks, your mouth ulcer hasn’t disappeared.
Symptoms

In most cases, mouth ulcers are easy to identify. They show up as sores on the roof of your mouth, inner cheeks, inner lips, gums, or tongue. Usually, mouth sores are: • Red around the edges. • The center can be white, yellow, or gray. There could be more than one ulcer, or you might just get one. The following are possible additional symptoms: • Swelling surrounding the ulcers. • More pain when you clean your teeth. • Pain that gets worse while consuming foods that are sour, salty, or spicy.
Causes
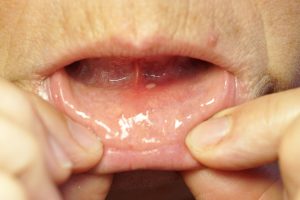
There are several causes of mouth ulcers, such as: • Minor tissue damage during dental procedures, such filling a cavity. • Biting your tongue or cheek by accident. • An adverse response to specific bacteria. • Donning retainers or braces. · Applying toothpaste that is abrasive or harsh. • Consuming a lot of acidic foods, like pineapples, oranges, and strawberries. • Changes in hormones during menstruation. dental braces• Tension. • Not getting enough sleep.
Prevention

For best oral health, brush your teeth twice a day and floss once a day. • To prevent tissue irritation, use a toothbrush with soft bristles. • Consume a balanced diet full with fresh produce. • Schedule routine dental examinations and cleanings. Treating your underlying disease can lower the chance of ulcers recurring if your doctor believes it is the cause of your sores. Discuss health management strategies with your healthcare practitioner.
Summary
The majority of mouth ulcers are not harmful. However, they can be a major annoyance. Pain from mouth sores might prevent you from doing the activities you love, such as kissing your partner, playing an instrument, eating particular foods, and drinking comfortably. It’s likely that your mouth ulcer will heal in two weeks. To ease pain until the sore heals, you can experiment with over-the-counter drugs and natural cures.