Parasitic infections are caused by organisms that live on or inside a host, drawing nutrients at the host’s expense. These infections are prevalent worldwide, with certain types more common in tropical and subtropical regions. While some parasitic infections cause mild discomfort, others can lead to severe illness or death if left untreated.
What Are Parasitic Infections?
Parasites are organisms that depend on a host for survival. Parasitic infections occur when these organisms invade the body, leading to various health problems. Parasites can be classified into three main types:
1. Protozoa: Single-celled organisms that multiply within the host, such as Plasmodium (malaria) and Giardia lamblia.
2. Helminths: Multicellular worms, such as tapeworms, roundworms, and flukes.
3. Ectoparasites: External parasites like lice, mites, and ticks.
Common Types of Parasitic Infections
1. Malaria
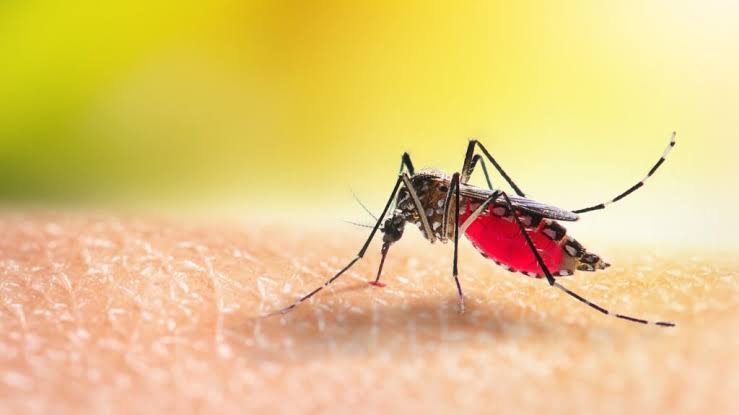
– Caused by Plasmodium parasites transmitted through mosquito bites.
– Symptoms include fever, chills, and fatigue, which can progress to severe complications if untreated.
2. Giardiasis
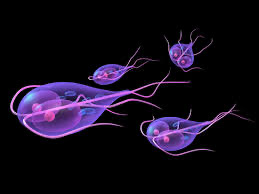
– Caused by Giardia lamblia through contaminated water or food.
– Symptoms include diarrhea, stomach cramps, and bloating.
3. Toxoplasmosis
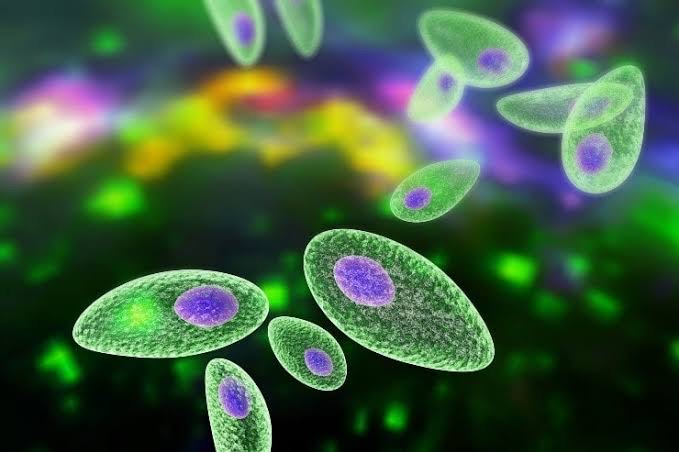
– Caused by Toxoplasma gondii, often through undercooked meat or contact with infected cat feces.
– Dangerous for pregnant women and individuals with weakened immune systems.
4. Ascariasis

– Caused by Ascaris lumbricoides, a type of roundworm.
– Common in areas with poor sanitation, leading to abdominal pain, malnutrition, and intestinal blockages.
5. Schistosomiasis
– Caused by blood flukes (worms) found in freshwater in certain regions.
– Symptoms include rash, fever, and long-term organ damage.
6. Lice and Scabies
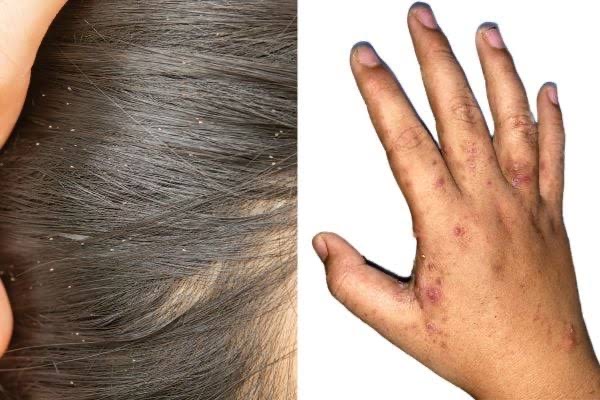
– Ectoparasites that cause itching and skin irritation.
– Spread through close contact or shared clothing and bedding.
How Do Parasitic Infections Spread?
Parasitic infections spread through:
– Contaminated food or water
– Insect bites (e.g., mosquitoes, ticks)
– Poor hygiene and sanitation
– Contact with infected soil, feces, or animals
Symptoms of Parasitic Infections
Symptoms vary depending on the parasite but may include:
– Diarrhea or constipation
– Abdominal pain and bloating
– Fatigue and weakness
– Itching or rash
– Fever and chills
– Weight loss
– Neurological symptoms (in severe cases)
Prevention of Parasitic Infections
1. Maintain Hygiene:
– Wash hands thoroughly with soap and water before eating and after using the toilet.
– Avoid touching your face with unclean hands.
2. Safe Food Practices:
– Cook meat thoroughly and wash fruits and vegetables before consumption.
– Avoid eating raw or undercooked seafood in high-risk areas.
3. Clean Water Access:
– Drink clean, filtered, or boiled water.
– Avoid swimming in or drinking from contaminated water sources.
4. Insect Protection:
– Use insect repellents and bed nets in areas prone to mosquito-borne diseases.
– Wear protective clothing to avoid insect bites.
5. Sanitation:
– Properly dispose of waste and avoid open defecation.
– Educate communities on hygiene practices.
Diagnosis and Treatment
Parasitic infections are diagnosed through laboratory tests, including stool samples, blood tests, and imaging. Treatment depends on the type of parasite and may involve:
– Antiparasitic Medications: Drugs like albendazole, ivermectin, or artemisinin for specific parasites.
– Symptomatic Treatment: Rehydration for diarrhea and antipyretics for fever.
– Surgical Intervention: In rare cases, for severe complications like intestinal blockages.
Conclusion
Parasitic infections pose a significant health challenge, especially in regions with poor sanitation and limited healthcare access. However, with proper hygiene, safe food and water practices, and public health interventions, many of these infections can be prevented. Early diagnosis and treatment are critical to managing symptoms and preventing long-term complications. Staying informed and vigilant is key to reducing the burden of parasitic infections globally.


Pingback: Cat Feces: What It Can Tell You About Your Pet’s Health - SimplExplainer