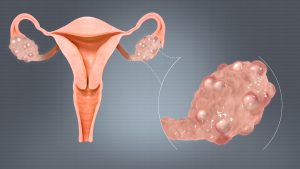
TREATMENT OF POLYCYSTIC OVARY SYNDROME
Treatment of polycystic ovary syndrome. One frequent disorder that affects your hormones is called polycystic ovarian syndrome, or PCOS. It results in infertility, acne, excessive hair growth, and irregular menstrual cycles. Whether or not you want to get pregnant will determine how you treat it. High blood pressure and diabetes are two illnesses that people with PCOS may be more susceptible to.
TREATMENT OF POLYCYSTIC OVARY SYNDROME
A hormonal imbalance known as polycystic ovarian syndrome is brought on by an overproduction of hormones by your ovaries, which are the organs responsible for producing and releasing eggs. Your ovaries create abnormally large amounts of androgens if you have PCOS. Your reproductive hormones become unbalanced as a result. Consequently, irregular menstrual cycles, missed periods, and uncertain ovulation are common in persons with PCOS. Because of anovulation, or the absence of ovulation, your ovaries may appear on ultrasound as small follicular cysts, which are fluid-filled sacs containing immature eggs.
Signs and Causes
1. Unusual periods

Missing or not having a period at all are examples of abnormal menstruation. Additionally, it could involve severe menstrual bleeding.
2. Abnormal hair growth
You may have hirsutism, or excessive facial hair, or you may have hirsutism, or heavy hair growth on your arms, chest, and belly. Up to 70% of PCOS patients experience this.
3. Acne
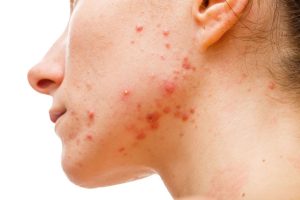
PCOS can lead to acne, particularly on the face, back, and chest. Acne can persist throughout adolescence and can be challenging to manage.
4. Obesity
Between 40% and 80% of PCOS patients struggle to maintain a healthy weight due to their obesity.
5. Skin darkening
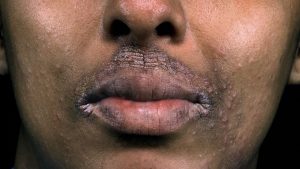
You may develop dark spots on your skin, particularly around your breasts, in the groin (the area between your legs), armpits, and neck folds. We call this acanthosis nigricans. •
6. Cysts
On ultrasound, the ovaries of many PCOS patients seem bigger or contain many follicles (egg sac cysts).
7. Skin tags
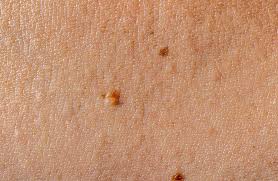
These are tiny, additional skin flaps. They frequently appear on your neck or in your armpits.
Hair loss
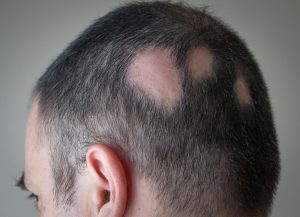
Individuals with PCOS may begin to go bald or lose patches of hair on their head.
8. Infertility
The most frequent cause of infertility in AFAB individuals is PCOS. The inability to conceive may be caused by irregular or infrequent ovulation.
Treatment
Hormonal birth control: options include intrauterine devices, vaginal rings, patches, injections, and pills. In addition to helping to control your menstrual cycle, several types of hormonal birth control can also help with acne and excessive hair growth. • Insulin-sensitizing medication: One medication used to treat diabetes is metformin. It functions by facilitating the body’s processing of insulin. Some PCOS patients experience improvements in their menstrual cycles once their insulin levels are under control. • Androgen-blocking drugs: A number of drugs can prevent the effects of androgens. This aids in managing hair growth or acne. Discuss with your doctor if this type of treatment is appropriate for you.
1. Lifestyle modifications
Insulin levels can be positively impacted by eating a healthy diet and keeping your body weight within a healthy range.
2. Ovulation-inducing drugs
Ovulation is the first step in a successful pregnancy. It has been demonstrated that some medications can cause ovulation in PCOS patients. Gonadotropins are administered via injection, whilst clomiphene and letrozole are taken orally.
3. Surgery
By excising the androgen hormone-producing tissue from your ovaries, surgery can help you resume ovulation. This technique is rarely carried out by surgeons due to the availability of newer drugs.
Summary
To learn more about your treatment plan and how to improve your chances of a safe pregnancy, speak with your healthcare professional.