
TYPES OF NEUROLOGICAL CONDITIONS
Types of neurological conditions. The World Health Organization defines neurological disorders as any illnesses that impact the nervous system as a whole. These disorders impact the neurons or tracts of the Central Nervous System in the Spinal Cord , the entire brain, or one of its components, such as the brain stem (Midbrain, Pons, and Medulla Oblongata), the cerebellum, the diencephalon, the basal ganglia, or the cortex.
TYPES OF NEUROLOGICAL CONDITIONS
Conditions that affect the way your nervous system which includes your brain, spinal cord, and nerves—functions are known as neurological illnesses. There are hundreds of neurological conditions, such as meningitis, multiple sclerosis, and Alzheimer’s disease. They produce symptoms that impact your thoughts, feelings, and movements. The type determines the available treatment options. Conditions that impact the way your nervous system works are known as neurological illnesses. Both your central and peripheral nerve systems are involved in this. Your brain and spinal cord are part of your central nervous system. All of the nerves that emerge from your spinal cord are part of your peripheral nervous system.
Types
1. Neurodegenerative diseases

Parkinson’s, multiple sclerosis, and Alzheimer’s
2. Neuromuscular disorder
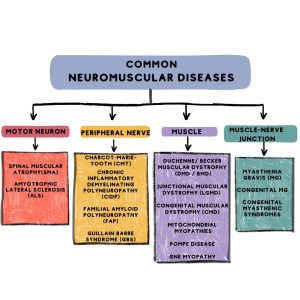
amyotrophic lateral sclerosis and muscular dystrophy.
3. Disorders of the brain
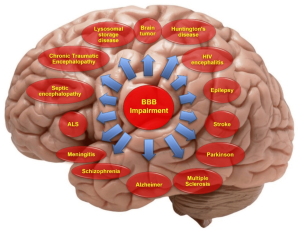
traumatic brain injury, migraines and headache disorders, epilepsy, and stroke.
4. Spinal disorders include spinal muscular atrophy, spinal cord damage, and spina bifida
5. Conditions affecting the peripheral nerves
include Bell’s palsy, carpal tunnel syndrome, and peripheral neuropathy.
Signs
Typical signs of neurological conditions include:
1. Pain
Neck, back, and headache pain.
2. Movement of the muscles

weakness, rigidity, tremor, spasms, paralysis, difficulties with coordination, and falls. •
3, Changes in sensitivity
loss of feeling, tingling, numbness, and hypersensitivity to warmth and touch.
4, Modifications to your senses
hallucinations, vertigo, loss of balance, ringing in your ears, hearing loss, smell and taste loss, vision loss, and double vision.
5. Sleep issues

include trouble falling asleep, excessive snoring, restless movements while sleeping, and daily drowsiness.
6. Alterations in consciousnes
coma, convulsions, and fainting.
7. Cognitive impairment
includes mood swings, memory loss, difficulty focusing, learning, or processing information, and confusion.
8. Speech and language impairments
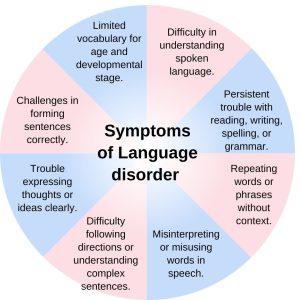
xr:d:DAFybrf3JVE:314,j:5930525705294329409,t:23120105
include slurred speech, slow speech, and trouble swallowing. • Breathing difficulties with little effort
Causes
Genetic alterations may be the cause of neurological diseases. • Congenital conditions, or abnormal neural system development. • Damage or injury to some nervous system components. • An infection. • A growth. • A stroke.
Treatment
Treatment for neurological problems could include: • Medications. • Making use of assistive technology. • Occupational therapy or physical therapy. • Speech therapy. • Surgery. • Taking part in clinical studies, which are human testing. Treatments differ greatly. Since there is no one-size-fits-all method of treatment, your healthcare practitioner will assist you in managing your unique symptoms. To help you make an informed decision about your health, your provider will go over the risks and side effects before you start treatment.
Prevention
Not all neurological conditions can be avoided. By maintaining your overall health and taking precautions when engaging in risky activities, such as wearing a helmet when participating in contact sports, you can lower your chance of suffering an injury or damaging your nervous system.
Summary
Being diagnosed with a neurological condition might be frightening. All of your physical processes, including your ideas, memories, emotions, and sensations, are controlled by your nervous system. Every neurological condition progresses differently; some may not affect your life at all, while others may necessitate round-the-clock care to reduce symptoms and avoid complications.