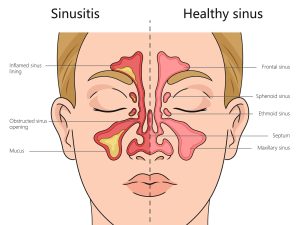
 What is sinusitis. A frequent ailment that can interfere with everyday living and cause severe discomfort is sinusitis. It can be easier to seek prompt treatment and implement preventive measures if one is aware of its causes and symptoms. A healthcare provider should assess chronic or severe symptoms to ensure proper treatment and care, even though many cases of sinusitis can be treated with over-the-counter drugs and home treatments.
What is sinusitis. A frequent ailment that can interfere with everyday living and cause severe discomfort is sinusitis. It can be easier to seek prompt treatment and implement preventive measures if one is aware of its causes and symptoms. A healthcare provider should assess chronic or severe symptoms to ensure proper treatment and care, even though many cases of sinusitis can be treated with over-the-counter drugs and home treatments.
WHAT IS SINUSITIS?
The inflammation of the sinuses, which are air-filled cavities in the facial bones surrounding the nose, is known as sinusitis. This inflammation, which is frequently brought on by bacterial or viral infections, allergies, or fungus, can obstruct the sinuses’ drainage channels and result in symptoms like pressure, facial pain, and a runny or stuffy nose. In addition, it may result in headaches, exhaustion, and a diminished sense of smell.
Causes;
1. Infections
– Viral Infections: The most common cause of sinusitis is a viral infection, such as the common cold.
– Bacterial Infections: Bacterial infections can develop if the sinuses remain blocked for an extended period.
– Fungal Infections: Fungal sinusitis is less common and typically occurs in people with weakened immune systems or allergies.
2. Allergies
– Allergic reactions to pollen, dust, mold, or pet dander can lead to inflammation and blockage of the sinuses.
3. Nasal Polyps
– These are small growths on the lining of the nasal passages or sinuses that can block the flow of mucus.
4. Deviated Septum
– A crooked septum, the wall between the nostrils, can restrict or block sinus passages.
5. Other Factors
– Other contributing factors include respiratory tract infections, smoking, and certain medical conditions like cystic fibrosis.
Symptoms;
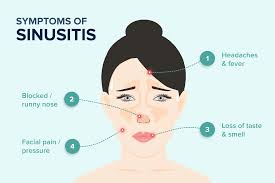
– Facial Pain and Pressure: Pain and tenderness around the eyes, cheeks, nose, or forehead.
– Nasal Congestion: Difficulty breathing through the nose due to blocked nasal passages.
– Runny Nose: Thick yellow or green nasal discharge.
– Headache: Pressure and pain in the head, often worsening when bending forward.
– Cough: A cough that may worsen at night.
– Fever: Low-grade fever may accompany sinusitis.
– Reduced Sense of Smell and Taste: Temporary loss or reduction in the ability to smell and taste.
– Bad Breath: Persistent bad breath or an unpleasant taste in the mouth.
Treatment;

MEANING OF SINUSITIS
1. Home Remedies
– Hydration: Drink plenty of fluids to thin mucus.
– Humidifiers: Use a humidifier or steam inhalation to keep sinuses moist.
2. Medications
– Decongestants: Over-the-counter decongestants can reduce nasal congestion but should be used for short periods.
– Nasal Corticosteroids: Sprays that reduce inflammation in the nasal passages.
– Pain Relievers: Over-the-counter pain relievers like ibuprofen or acetaminophen can alleviate pain and reduce fever.
3. Medical Procedures
– Nasal Irrigation: A saline solution rinse to clear mucus and debris from the nasal passages.
– Surgery: In chronic or severe cases, surgery may be necessary to remove blockages or correct structural problems in the sinuses.
Prevention;

MEANING OF SINUSITIS
1. Avoid Allergens: Minimize exposure to allergens by keeping your environment clean and using air purifiers.
2. Good Hygiene: Wash hands regularly to prevent infections.
3. Humidify Air: Use a humidifier to maintain moist air in your home, especially in dry climates.
Summary
An inflammation or swelling of the tissue lining the sinuses is called sinusitis, sometimes referred to as a sinus infection. Although healthy sinuses are full of air, bacteria can develop and cause an infection if they become clogged and filled with fluid. The causes, signs, and remedies of sinusitis are examined in this article.