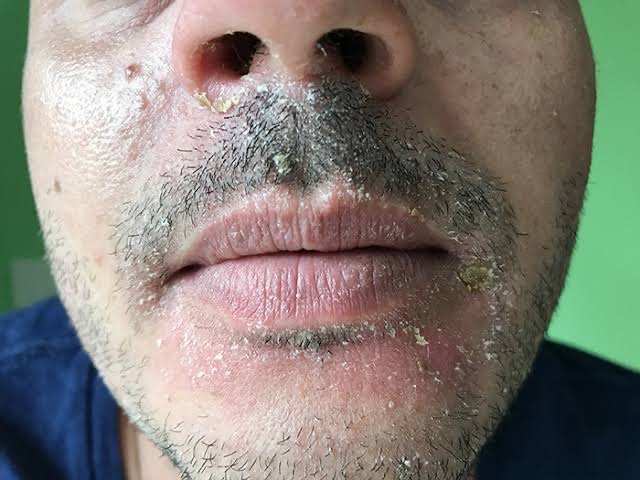
Seborrheic dermatitis is a common skin condition that causes red, scaly, and itchy patches, often affecting the scalp, face, and other oily areas of the body. It is a chronic condition that can flare up periodically but can be managed with proper treatment.
Causes of Seborrheic Dermatitis
While the exact cause is unknown, several factors contribute to seborrheic dermatitis:
– Overactive Sebaceous Glands: Excess oil production can trigger symptoms.
– Fungal Overgrowth (Malassezia): A naturally occurring yeast on the skin can multiply excessively, leading to irritation.
– Genetics: Family history may increase the risk.
– Weather Conditions: Cold, dry weather can worsen symptoms.
– Stress and Hormonal Changes: Can trigger or worsen flare-ups.
– Certain Medical Conditions: More common in people with Parkinson’s disease, HIV/AIDS, or weakened immune systems.
Symptoms of Seborrheic Dermatitis
Symptoms vary in severity and may include:
– Scaly patches with greasy or flaky skin (commonly on the scalp, eyebrows, sides of the nose, and ears).
– Red, irritated skin in affected areas.
– Persistent dandruff that may be difficult to control.
– Itching or burning sensation on the scalp or other areas.
– Worsening symptoms in cold or stressful conditions.
Seborrheic Dermatitis vs. Other Skin Conditions
Seborrheic dermatitis is often confused with other skin conditions, such as:
– Dandruff: A milder form affecting only the scalp.
– Psoriasis: Similar scaly patches but usually thicker and more widespread.
– Eczema: Causes more intense itching and dryness.
Treatment for Seborrheic Dermatitis
Although there is no permanent cure, treatment can help manage symptoms effectively.
1. Medicated Shampoos (For Scalp Seborrheic Dermatitis)
– Anti-fungal Shampoos: Contain ketoconazole, selenium sulfide, or zinc pyrithione to reduce yeast overgrowth.
– Coal Tar Shampoos: Slow down skin cell turnover and reduce scaling.
– Salicylic Acid Shampoos: Help remove dead skin and flakes.
2. Topical Treatments (For Face and Body)
– Antifungal Creams: Ketoconazole or ciclopirox creams help control yeast growth.
– Corticosteroid Creams: Reduce inflammation and redness but should be used sparingly to avoid side effects.
– Calcineurin Inhibitors: Tacrolimus and pimecrolimus are alternatives to steroids for sensitive areas like the face.
3. Lifestyle and Home Remedies
– Wash Affected Areas Gently: Use mild, fragrance-free cleansers to avoid irritation.
– Moisturize Regularly: Helps reduce dryness and scaling.
– Manage Stress: Stress can trigger flare-ups, so relaxation techniques like meditation or exercise may help.
– Avoid Harsh Hair Products: Alcohol-based or fragranced products can worsen symptoms.
– Maintain a Healthy Diet: Some people find that limiting processed foods and eating anti-inflammatory foods (like omega-3-rich fish) helps reduce flare-ups.
When to See a Doctor
If symptoms persist despite home treatments, or if seborrheic dermatitis becomes severe and affects daily life, consulting a dermatologist is recommended. Prescription-strength treatments may be necessary for better symptom control.
Conclusion
Seborrheic dermatitis is a manageable but chronic condition that can cause discomfort if left untreated. With the right combination of medicated shampoos, topical treatments, and lifestyle adjustments, most people can keep symptoms under control and prevent flare-ups.