Barley nutritional benefits. It is a great supplement to any diet because of its historical roots and contemporary nutritional advantages. Numerous health advantages and culinary opportunities are provided by its high fiber content, vital vitamins and minerals, and adaptability in the kitchen. Barley is a tasty and nutritious grain that can improve any meal, whether it is used in soups, salads, baked products, or drinks.
BARLEY NUTRITIONAL BENEFITS
For thousands of years, barley—one of the earliest cereals to be cultivated—has been a staple diet. Barley, scientifically known as Hordeum vulgare, was an essential crop in ancient societies such as the Greeks, Romans, and Egyptians. It is still prized today for its many health advantages, strong nutritional profile, and culinary adaptability.
Nutritional Benefits;

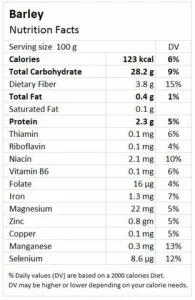
Barley is celebrated for its high fiber content, particularly beta-glucan, a soluble fiber known for its cholesterol-lowering properties. Consuming barley regularly can help reduce bad cholesterol levels and support heart health. Barley is also rich in essential vitamins and minerals, including magnesium, phosphorus, selenium, and B vitamins. Additionally, barley provides a good source of plant-based protein and various antioxidants, which can help protect against chronic diseases and inflammation.
Types of Barley;

BARLEY NUTRITIONAL BENEFITS
Hordeum vulgare is available in several forms, each offering different textures and cooking times:
– Hulled Barleys: The whole grain form of barley with only the outermost hull removed, retaining the bran and germ layers. It has a chewy texture and is the most nutritious form.
– Pearled Barleys: The bran layer is removed, making it quicker to cook and less chewy than hulled barley. It is the most commonly used form in cooking.
– Barley’s Flakes: Flattened and cut barley kernels, similar to rolled oats, used in cereals and baking.
– Barley Flour: Ground barley used in baking and cooking to add a nutty flavor and nutritional benefits.
Culinary Uses;

BARLEY NUTRITIONAL BENEFITS
Hordeum vulgare versatility makes it a valuable ingredient in various dishes. It is often used in soups and stews, adding a hearty texture and nutritional boost. Hordeum vulgare can also be cooked as a grain side dish, similar to rice or quinoa, or added to salads for a chewy, nutty element. Barley’s flour is used in baking, particularly in bread and muffins, to enhance flavor and nutritional content. Additionally, barleys are a key ingredient in the production of beer and whiskey, showcasing its importance beyond the kitchen.
Health Benefits;

BARLEY NUTRITIONAL BENEFITS
Beyond its heart-healthy properties, It offers numerous other health benefits. Its high fiber content aids in digestion, promotes regular bowel movements, and helps maintain a healthy weight by promoting a feeling of fullness. Barleys also has a low glycemic index, making it beneficial for blood sugar control and a good choice for people with diabetes. The antioxidants found in barleys can help reduce inflammation and protect against certain diseases, supporting overall health and well-being.
Summary
Barley has many health advantages, such as better blood sugar regulation, improved heart health by lowering blood pressure and cholesterol, and improved digestion because of its high fiber content. Additionally, it contains important minerals like phosphorus and magnesium, promotes bone health, and helps control weight by boosting satiety.