
Major nurse requirements. A solid intellectual background in science and arithmetic is a prerequisite for major nursing programs; biology, chemistry, physics, English, and mathematics are frequently required in high school or as preparatory courses. After that, in order to be licensed, candidates usually need to complete a degree program, such as an Associate’s Degree in Nursing (ADN) or a Bachelor of Science in Nursing (BSN), and pass the NCLEX-RN exam. Additional graduate study is required for advanced positions.
MAJOR NURSE REQUIREMENTS
Starting a nursing career is an honorable and fulfilling path, but it has prerequisites to guarantee skill and higg quality patient care. This in depth blog post will walk you through all of the prerequisites for becoming a nurse, including training, certification, and personal qualities that are essential for success in this fast-paced field of healthcare.
Educational Requirements;
1. High school Diploma or Equivalent:

Getting a high school diploma or its equivalent, such as a general Educational Development (GED) certificate, is the first requirement for becoming a nurse. It can help to have solid background in biology, chemistry and mathematics.
2. Prerequisite College Courses:
Completing prerequisite course in anatomy, physiology, microbiology, and psychology is mandatory for many nursing programs. The fundamental knowledge required for nursing education is covered in these courses.
Nursing Degree Programs:

To become a nurse, one can follow one of several different educational pathways, each with specific requirements:
Nursing diploma:
A few hopital provide two to three year nursing diploma programs. These days, though this path is less typical.
Bachelor of Science in Nursing:

University based BSN programs normally last four years. BSN holders are more in demand in the nursing field and frequently have wider job options.
Clinical Experience And Training;
Clinical Rotations:
As part of the nursing curriculum, students participate in practical clinical rotations that enable them to apply their theoretical knowledge in actual healthcare settings. These rotations include a wide range of disciplines, including pediatrics, obstetrics, and medical-surgical nursing.
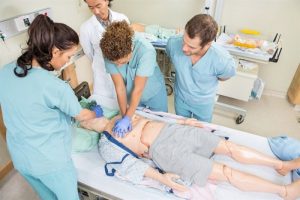
Simulation Labs:
Major nurse requirements
A lot of nursing programs include simulation labs where students can hone their abilities in a safe setting. This offers a secure environment for honing clinical skills prior to working with real patients.
Professional Attributes And Skills:
Effective Communication:
Being able to communicate well is essential for nurses. To guarantee coordinated and thorough care, nurses must communicate openly and effectively with patients, families, and other medical professionals.
Empathy & Compassion:

Major nurse requirements
As a compassionate vocation, nursing requires the capacity to sympathize with patients during difficult situations. In addition to fostering trust, compassion improves patient outcomes.
Critical Thinking:

Major nurse requirements
In order to evaluate situations, make wise judgments, and efficiently prioritize treatment, nurses need to be very proficient in critical thinking. Rapid thinking is frequently needed in fast-paced healthcare settings
Summary
You will be taught how to study patients and determine their needs from the beginning of your course until your first employment. You’ll learn how to prepare and provide the best treatment possible for them, as well as assess the outcomes. It’s crucial to establish a connection of trust with every patient. Regardless of their circumstances, you want to help them live better lives. To attain the best outcomes for your patients, you will need to balance a number of priorities and consider a lot of factors.


Pingback: 5 Common Mistakes to Avoid When Starting a Podcast - SimplExplainer