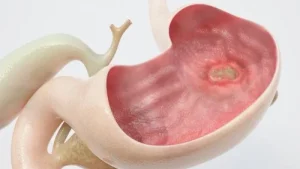
Causes and types of ulcers. Certain ulcers, such as arterial ulcers, may not heal at all or may take months to resolve. With the right care, some kinds, such as stomach or peptic ulcers, can recover in as little as one month. A painful sore that heals slowly and occasionally recurs is called an ulcer. Ulcers are not rare. Usually, their underlying reasons determine why they manifest and the symptoms that go along with them. From the outside layer of your skin to the lining of your stomach, ulcers can develop anywhere on your body.
CAUSES AND TYPES OF ULCERS
Slow-healing sores that occasionally recur are called ulcers. They can show up anywhere in the body, from the vaginal area to the lining of the stomach. Although peptic ulcers are the most prevalent type of ulcer, there are other varieties as well, and many of them are brought on by underlying medical issues. The source of ulcers determines how to treat them. The discomfort that ulcers may cause can be lessened with over-the-counter remedies. You might get relief from your problems more quickly if you discuss them with your doctor as soon as possible.
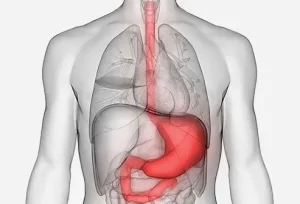
CAUSES AND TYPES OF ULCERS
Peptic ulcers, another name for ulcers, are open sores in the upper portion of the small intestine or stomach lining. The mucus lining the inside of your digestive tract becomes eroded by stomach acid, resulting in the formation of an ulcer.
Types of peptic ulcers’
1. Gastric ulcer: It happens when a sore develops in the stomach lining.
2. Duodenal ulcer: This is the result of an upper intestinal sore developing.
3. Esophageal ulcer:
CAUSES AND TYPES OF ULCERS
Also, prior until the mid 1980s, the general consensus was the ulcers were caused by stress, a genetic predisposition to increased acid secretion, and unhealthy lifestyle choices ( such as bingeing on rich, fatty foods, alcohol, caffeine and smoke). It was thought that these conditions would cause an accumulation of stomach acids which could damage the lining that protects the stomach, duodenum, or esophagus.
Although excessive release of acid undoubtedly contributes to the formation of ulcers, a more recent idea suggests that bacterial infection is the main cause of peptic ulcers. since the mid 1980s, research has indicated over 80% of stomach ulcers and over 90% of duodenal ulcers are caused by the bacteria Helicobacter pylori, or H. pylori more recent data, though, shows that those percentages are falling.
However, most likely, you’ll have discomfort or scorching ache between your breastbone and belly button. When you’re empty handed, such at night or in between meals, you can sense it more than usual. If you take an antacid, the pain can go away for a short while, but it might come back.
The discomfort may come and go for several days or weeks, lasting a few minutes or several hours.
Other symptoms include:
CAUSES AND TYPES OF ULCERS
1. Easily feeling satisfied
2. Pain preventing you from wanting to eat reflux
3. Acid reflux chest ache weary
4. Feeling bloated Burping
5. Absence of hunger or reduction in weight emesis dark or bloody excrement
Summary
The primary causes of ulcers are H. pylori bacterial infections and chronic nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) use, both of which can harm the stomach and small intestine’s protective lining. Although there are many distinct kinds of ulcers, the most common ones are peptic ulcers (stomach or duodenum) and skin ulcers, including pressure, venous, arterial, and neuropathic ulcers.