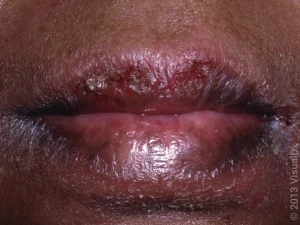
Lip breakage causes and treatments. Dry or cold weather, dehydration, the sun, lip licking, certain medications, vitamin deficiencies (B, iron, and vitamin A toxicity), allergies, or infections can all result in lip breaking (chapped or cracked lips). Regular use of SPF/moisturizing lip balms (shea butter, oils, petrolatum), drinking enough of water, refraining from licking, and using humidifiers are all part of the treatment; severe instances require medical attention.
LIP BREAKAGE CAUSES AND TREATMENTS
Lip breaking is a frequent problem that may be both irritating and ugly. It is characterized by dryness, cracking, and peeling. Environmental variables, lifestyle choices, or even underlying medical conditions are frequently the cause of this illness. You can keep your lips healthy and supple all year long by knowing what causes lip breakage and how to repair it.
Common Causes;
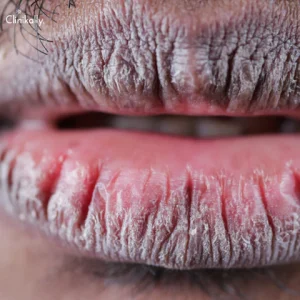
1. Dehydration:
One of the primary causes of chapped lips is dehydration. When your body lacks sufficient water, your lips are one of the first areas to show signs of dryness.
2. Cold and Dry Weather:
Cold winds and dry air can strip moisture from your lips, leading to cracking and peeling, especially during winter months.
3. Excessive Licking or Biting:
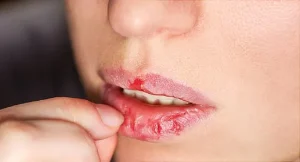
Lip breakage causes and treatments
While it might seem like licking your lips would help keep them moist, it actually has the opposite effect. Saliva evaporates quickly, leaving lips drier than before. Biting your lips can also cause irritation and worsen breakage.
4. Irritating Ingredients in Lip Products:
Some lip balms, lipsticks, or glosses contain ingredients like menthol, camphor, or fragrances that can irritate sensitive skin, leading to further dryness and cracking.
5. Vitamin Deficiency:

Lip breakage causes and treatments
A lack of essential vitamins, particularly B vitamins, can lead to dry, cracked lips. Vitamin B2 (riboflavin) deficiency is especially known to cause chapped lips.
Effective Treatments;
1. Stay Hydrated:
Drink plenty of water throughout the day to keep your body and lips hydrated. This is one of the most effective ways to prevent and treat chapped lips.
2. Use a Nourishing Lip Balm:

Lip breakage causes and treatments
Choose a lip balm that contains moisturizing ingredients like beeswax, shea butter, coconut oil, or hyaluronic acid. Avoid balms with irritating ingredients like menthol or strong fragrances.
3. Exfoliate Gently:
Exfoliating your lips can help remove dead skin cells and promote healing. Use a gentle lip scrub or make your own by mixing sugar with a small amount of honey. Apply the scrub in circular motions and rinse off with lukewarm water.
4. Protect Your Lips from the Elements:

Lip breakage causes and treatments
In cold or windy weather, apply a thick, protective lip balm before going outside. Look for products with SPF to protect your lips from UV damage, even in winter.
5. Avoid Licking or Biting Your Lips:
Break the habit of licking or biting your lips. If you find it difficult, try keeping a moisturizing lip balm handy to apply whenever you feel the urge.
6. Improve Your Diet:

Lip breakage causes and treatments
Ensure your diet includes foods rich in B vitamins, such as eggs, lean meats, nuts, and leafy greens. If necessary, consider taking a vitamin B complex supplement after consulting with a healthcare provider.
Summary
Breakage of the lips is a common but controllable problem. You can maintain the softness, smoothness, and health of your lips by treating the underlying causes, which may include food, environmental exposure, or dehydration. Chapped lips can be prevented and treated with regular hydration, nourishing lip balms, and weather protection.
Pingback: Natural Hair Growth and Strengthening SupplementS - SimplExplainer