Glycated hemoglobin, or HbA1c, is a vital indicator used in the detection and treatment of diabetes. This article will examine glycogen hemoglobin, including definition, relevance, measurement, and implications for diabetics.
What is HbA1c?
Hemoglobin is a protein in red blood cells responsible for carrying oxygen throughout the body. When glucose (sugar) enters the bloodstream, it can attach to hemoglobin, forming glycated hemoglobin. The amount ofglycated hemoglobin formed is directly proportional to the average concentration of glucose in the blood over a period of approximately three months, the typical lifespan of a red blood cell.
Significance of glycated hemoglobin
1. Diagnosis of Diabetes
• The HbA1c test is used to diagnose prediabetes and diabetes. A higher glycated hemoglobin level indicates poorer blood sugar control and a higher risk of diabetes-related complications.
2. Monitoring Blood Glucose Control
• For individuals already diagnosed with diabetes, the test is a reliable measure of how well blood sugar levels have been controlled over time. It helps in assessing the effectiveness of diabetes management plans, including medication, diet, and exercise.
3. Predicting Complications
• Persistent high levels of glycated hemoglobin are associated with an increased risk of complications such as cardiovascular disease, neuropathy, nephropathy, and retinopathy. Therefore, maintaining an HbA1c level within the target range is crucial for reducing these risks.
How is HbA1c Measured?
The HbA1c test is a simple blood test. It doesn’t require fasting and can be done anytime of the day. The test is usually run in a lab, but point-of-care testing kits can also be used in clinics and, in certain situations, at home.
Understanding glycated hemoglobin Results
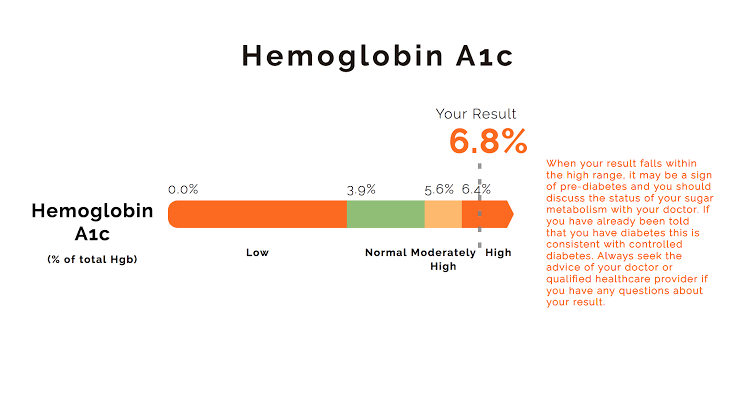
– Normal Range
– An HbA1c level below 5.7% is considered normal.
Prediabetes
• An HbA1c level between 5.7% and 6.4% indicates prediabetes, suggesting an increased risk of developing diabetes.
• Diabetes
– An HbA1c level of 6.5% or higher on two separate tests confirms a diagnosis of diabetes.
Target HbA1c Levels
For individuals with diabetes, the target level may vary depending on several factors, including age, duration of diabetes, presence of other health conditions, and individual patient factors. Generally, the American Diabetes Association (ADA) recommends a target HbA1c of less than 7% for most adults with diabetes. However, more stringent (<6.5%) or less stringent (<8%) targets may be appropriate for certain individuals based on their specific circumstances.
Factors Affecting HbA1c Levels
1. Blood Sugar Control
• Effective management of blood glucose levels through medication, diet, and exercise is crucial for maintaining a desirable level.
2. Red Blood Cell Lifespan
• Conditions that affect the lifespan of red blood cells, such as hemolytic anemia or recent blood transfusions, can impact it’s results.
3. Other Medical Conditions
• Conditions like chronic kidney disease or liver disease can also affect it’s levels.
Tips for Managing HbA1c Levels
1. Regular Monitoring
• Regularly check blood glucose levels and have HbA1c tested as recommended by your healthcare provider (usually every 3-6 months).
2. Healthy Diet
• Follow a balanced diet rich in whole grains, fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and healthy fats. Limit intake of sugary foods and beverages.
3. Physical Activity
• Engage in regular physical activity, such as brisk walking, swimming, or cycling, to help control blood sugar levels.
4. Medication Adherence
• Take diabetes medications as prescribed and discuss any concerns or side effects with your healthcare provider.
5. Lifestyle Modifications
• Manage stress, avoid smoking, and limit alcohol consumption.
HbA1c is a vital tool in the diagnosis and management of diabetes, providing a long-term view of blood sugar control. By understanding the significance of HbA1c and taking proactive steps to manage it, individuals with diabetes can significantly reduce their risk of complications and improve their overall quality of life. Regular monitoring and a comprehensive diabetes management plan are key to achieving and maintaining optimal HbA1 levels.