
BENEFITS OF SELF CONTROL
Benefits of self control. Self-control is a highly sought-after quality that all too frequently eludes us, according to many people. There are many aspects of daily life that many of us wish to improve. With millions of individuals making New Year’s resolutions every year, this is very clear. These resolutions frequently include objectives pertaining to relationships, money, nutrition and fitness, and cutting back on bad habits. Self-control is a highly sought-after quality that all too frequently eludes us, according to many people.
BENEFITS OF SELF CONTROL
There are many aspects of daily life that many of us wish to improve. The study supporting the interchangeability of the terms self-control and its many advantages, as well as how to achieve them, will be examined in this article. There will also be descriptions of a number of intriguing research studies. In addition to helping, you become more compassionate and kinder to yourself, these thorough, scientifically grounded activities will equip you with the skills you need to help your clients, students, or staff become more compassionate toward themselves.
1. Health, Fitness, and Weight

Eating has been described as the greatest obstacle to self-control. The massive industry surrounding weight loss is evident from the constant barrage of advertisements for gym memberships, self-discipline exercise, weight loss programs, and even weight loss surgery. Not to mention the difficulties many people personally face because of their weight. Measures of self-control throughout youth have also been connected to medical issues in maturity. More precisely, worse self-control was associated with increased risk for cancer, high blood pressure, asthma, stuttering speech patterns, depression, other mental diseases, impaired hearing, and high cholesterol.
2. Success in School and the Workplace

Self-control has a significant impact on children’s schooling in addition to health-related results. Many people are working from home as a result of the quick advancements in office automation technology. Employees can benefit from telecommuting in many ways, including greater freedom, but there are drawbacks as well. First and foremost, workers may be less productive if they are working in an atmosphere that could be distracting without direct supervision. Employees do, in fact, need a certain level of drive and self-discipline to succeed in their positions.
3. Dangerous and Troublesome Conduct

self-control theory is frequently discussed in behavioral theories that aim to explain abnormal, harmful, and dangerous behaviors. Adequately self-controlled people are less likely than their less-controlled counterparts to pay attention to or invest in these aspects of a scenario.
4. Results Associated with Self-Control
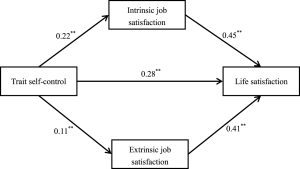
Higher self-control was linked to stronger interpersonal and relational skills, a higher-grade point average, fewer binge eaters, more stable attachments, and better adjustment as measured by higher self-esteem and less psychopathology, according to the findings.
5. Healthy Decisions

When we are emotionally dysregulated or feel vulnerable, we frequently make bad decisions. Sometimes, when we are going through difficult circumstances, we make bad decisions about our relationships, eating, or leisure activities. Additionally, several actions frequently exacerbate or intensify the initial unpleasant feeling.
6. Positive Communication

This is worth having! People who communicate from an unpleasant emotional reaction are motivated by negative forces. While screaming and yelling might undoubtedly be a part of it, this is not the only indication. Your communication of personal wants and desires will be hindered if you feel inadequate. Naturally, that will cause you to be unhappy in your relationships or at work.
Summary
If you are reading this, you are probably old enough that when you experience emotional distress, your brain is hardwired to respond in a particular way. You’ve been doing this for years and years. The good news is that you have the power to change. All you need is a personal will to change, and some guidance.