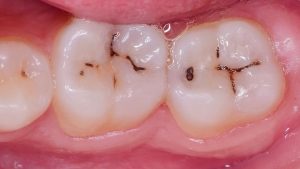
Decay of tooth. For this to be effectively treated and additional harm to be avoided, early detection is essential. Frequent dental examinations enable dentists to see decay early and take the necessary precautions before cavities worsen and cause discomfort. Reducing the prevalence of dental decay is largely dependent on public knowledge of its causes, prevention, and treatment. Healthy eating habits and proper dental hygiene can be encouraged from an early age through educational programs, particularly for parents and kids.
DECAY OF TOOTH
Tooth decay, also known as dental caries or cavities, is a common dental problem affecting people of all ages. It is the destruction of the tooth structure due to the action of acids produced by bacteria in the mouth. This article will explore the causes, prevention, and treatment of tooth decay.
Causes;
1. Bacteria in the Mouth;
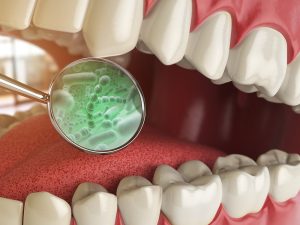
• The primary cause of it is the presence of specific bacteria, such as Streptococcus mutans, which thrive on the sugars and starches left on teeth from food and drinks.
2. Formation of Plaque;
• Plaque is a sticky film that forms on teeth when bacteria feed on sugars and produce acids. If not removed regularly, plaque hardens into tartar, which can only be removed by a dentist.
3. Acid Production;
• The acids produced by bacteria attack the tooth enamel, the hard outer surface of the tooth. Over time, repeated acid attacks weaken the enamel, leading to the formation of cavities.
4. Diet;
• Frequent consumption of sugary and starchy foods and beverages contributes significantly to tooth decay. These foods provide the fuel that bacteria need to produce acids.
5. Poor Oral Hygiene
• Inadequate brushing and flossing allow plaque to build up on teeth, increasing the risk of decay.
Prevention of Tooth Decay;
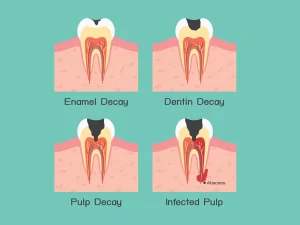
DECAY OF TOOTH
1. Good Oral Hygiene Practices;
– Brush your teeth at least twice a day with fluoride toothpaste.
– Floss daily to remove plaque and food particles between teeth.
– Use an antibacterial mouthwash to reduce the bacterial load in the mouth.
2. Healthy Diet;

DECAY OF TOOTH
– Limit sugary and starchy foods and beverages.
– Eat a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and dairy products to support overall oral health.
3. Regular Dental Visits;
– Visit your dentist regularly for check-ups and professional cleanings. Early detection of cavities allows for more straightforward and less invasive treatments.
4. Fluoride Use;

DECAY OF TOOTH
– Use fluoride toothpaste and drink fluoridated water if available. Fluoride strengthens tooth enamel and makes it more resistant to it.
5. Dental Sealants;
– Dental sealants are a protective coating applied to the chewing surfaces of the back teeth. They can prevent food and bacteria from getting trapped in the grooves of the teeth.
Treatment;
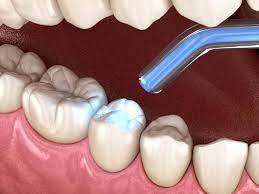
DECAY OF TOOTH
1. Fluoride Treatments
• For early-stage, fluoride treatments can help remineralize the enamel and stop the progression of cavities.
2. Fillings
• For more advanced decay, a dentist will remove the decayed portion of the tooth and fill the cavity with materials such as amalgam, composite resin, or gold.
3. Crowns
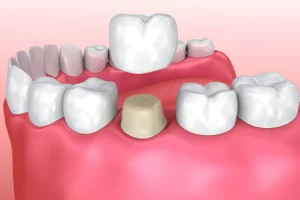
DECAY OF TOOTH
• If the decay is extensive and has weakened the tooth, a crown (a cap that covers the tooth) may be necessary to restore its shape, strength, and function.
Summary
A nutritious diet, frequent dental checkups, preventive treatments, and proper oral hygiene are all necessary to avoid it. People can take proactive measures to preserve their oral health and prevent the discomfort and consequences linked to cavities by being aware of the causes and symptoms of it. Maintaining a beautiful, healthy smile requires early intervention and routine dental care.