
Academic writing. Gaining proficiency in academic writing is essential for improving your capacity to express difficult concepts in an understandable and convincing manner. You can succeed in your scholarly activities and make a significant contribution to your academic field by comprehending the essential components of academic writing, practicing frequently, and aiming for constant growth. The ideas presented in this guide will assist you in producing excellent, influential academic work, whether you are writing research papers, essays, or dissertations.
ACADEMIC WRITING
The foundation of scholarly communication is academic writing, which promotes the sharing of concepts, discoveries, and critical analysis across a variety of subject areas. For professionals, researchers, and students who want to contribute to their academic communities, mastering this style of writing is crucial. This guide offers advice and techniques to improve your writing abilities while examining the essential components of academic writing.
Understanding;

It is characterized by its formal tone, clear focus, and structured organization. It serves multiple purposes, including:
1. Communicating Research: Presenting original research findings in a clear and concise manner.
2. Analyzing Ideas: Critically examining theories, arguments, and evidence.
Key Elements;

1. Clarity and Precision
– Use clear and concise language to express ideas effectively.
– Avoid ambiguous terms and jargon unless specifically defined.
– Focus on logical flow and coherence to ensure that each part of the paper contributes to the overall argument.
2. Formal Tone
-Maintain a formal, objective tone, avoiding colloquial expressions and personal opinions unless specified.
– Use third-person perspective, except in disciplines where first-person is accepted.
3. Structured Organization
– Follow a standard structure: introduction, body, and conclusion.
– Use headings and subheadings to organize content and guide the reader.
– Ensure each paragraph transitions smoothly to the next, maintaining a logical progression of ideas.
4. Evidence-Based Arguments
– Support claims with credible evidence, including data, research studies, and expert opinions.
– Evaluate sources for reliability and relevance.
– Integrate evidence seamlessly into your argument, explaining its significance.
5. Proper Citation
– Use the appropriate citation style (APA, MLA, Chicago, etc.) as specified by your institution or publication.
– Include in-text citations and a comprehensive bibliography or reference list.
– Avoid plagiarism by properly attributing all sources.
Types;
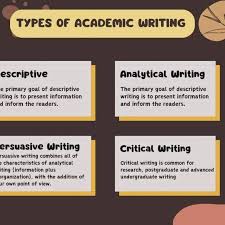
Academic writing
1. Research Papers
– Present original research, including methodology, results, and discussion.
– Follow a structured format: abstract, introduction, literature review, methods, results, discussion, conclusion.
2. Essays
– Explore a specific question or topic through analysis and argumentation.
– Common structures include argumentative, descriptive, expository, and narrative essays.
3. Literature Reviews

Academic writing
– Summarize and critically evaluate existing research on a particular topic.
– Identify gaps in the literature and suggest areas for future research.
4. Theses and Dissertations
– Extensive research projects required for advanced degrees.
– In-depth exploration of a specific research question or hypothesis, demonstrating the ability to conduct independent research.
Effectice tips;

Academic writing
1. Plan and Outline
– Begin with a clear thesis statement or research question.
– Create an outline to organize your thoughts and structure your paper.
– Break the writing process into manageable sections and set deadlines for each.
2. Draft and Revise
– Write a first draft without worrying about perfection.
– Focus on getting ideas down, then refine through multiple revisions.
-Seek feedback from peers, mentors, or writing centers.
Summary
Research-based arguments and evidence are the main focus of academic writing, a formal, objective writing style utilized in academic institutions and publications. It frequently uses technical vocabulary unique to a subject of study and is well-structured, precise, and easy to understand. Important features include a formal tone, the use of the third person, and an emphasis on concepts and facts rather than feelings or personal judgments.


Pingback: Tooth Decay: Causes, Prevention, and Treatment - SimplExplainer
Pingback: Decay of Tooth - SimplExplainer