
Sleep and neck pains. Poor sleeping positions (particularly stomach sleeping), unsupportive pillows or mattresses, bad posture during the day (such as slouching at computers), stress, dehydration, and underlying conditions (such as arthritis or pinched nerves) all strain neck muscles, causing stiffness and pain. However, proper alignment (back/side sleeping), supportive pillows, gentle stretches, and occasionally heat/cold therapy can provide relief and prevention. Waking up with neck pain is a common issue that many people experience. This discomfort often stems from poor sleep posture or an unsupportive pillow, which can strain the muscles and joints in the neck.
SLEEP AND NECK PAINS
Cervicalgia, also known as neck pain, is frequently caused by bad posture, strain, or uncomfortable sleep. It can also result from arthritis, herniated discs, injuries (such as whiplash), or infections. It usually gets better with at-home treatments like gentle movement, hot or cold packs, and over-the-counter medications, but it needs to be treated by a doctor if it is severe, occurs after trauma, or results in numbness or weakness.
Causes;

Neck pain from sleep can arise from several factors:
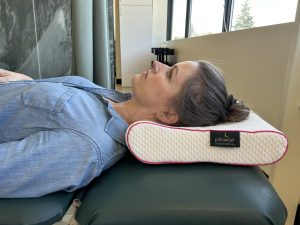
– Sleep Position: Sleeping on your stomach can place unnecessary strain on the neck. Side and back sleepers may also experience pain if their head is positioned awkwardly.
– Pillow Quality: An unsupportive pillow or one that is too high or low can cause misalignment of the neck and spine.
– Mattress Firmness: A mattress that is too firm or too soft can affect spinal alignment and lead to neck pain.
– Muscle Strain: Inadequate support or an awkward sleeping position can cause muscle strain, resulting in stiffness and discomfort upon waking.
Prevention;

To prevent neck pain from sleep, consider the following tips:
– Choose the Right Pillow: Opt for a pillow that supports the natural curve of your neck. Memory foam or adjustable pillows can offer better support.
– Maintain Proper Sleep Posture: Sleeping on your back or side with proper alignment can help. Avoid sleeping on your stomach.
1 Use a Supportive Mattress: Ensure your mattress provides adequate support for spinal alignment.
– Adjust Sleep Environment: Make sure your pillow and mattress are neither too high nor too low, and maintain a comfortable sleeping temperature.
Relief;
Sleep and neck pains
If you wake up with neck pain, several remedies can help alleviate discomfort:
– Gentle Stretching:
Perform gentle neck stretches and exercises to relieve tension and improve flexibility.
– Heat or Cold Therapy:

Sleep and neck pains
Apply a warm compress or ice pack to the affected area to reduce pain and inflammation.
– Over-the-Counter Pain Relief:
Non-prescription pain relievers like ibuprofen or acetaminophen can help manage pain.
– Professional Help:

Sleep and neck pains
If the pain persists, consider consulting a healthcare professional for a tailored treatment plan.
Neck pain from sleep is often manageable with simple adjustments to your sleeping habits and environment. Paying attention to your pillow, mattress, and sleep posture can significantly reduce discomfort and improve your overall sleep quality.
Summary
The brain and body repair, consolidate memories, regulate hormones, and support immune function during cycles of non-REM (light to deep) and REM sleep. Most adults require 7-9 hours of sleep per night for optimal well-being, mood, and cognitive performance. Sleep is an essential, natural state of rest that is necessary for both physical and mental health.