Causes of blurry vision. The retina is the thin layer of tissue at the back of the eye that receives and processes light to convey visual signals to the brain. Retinal disorders are a collection of ailments that damage the retina. Retinal damage or disturbances can significantly impair vision and, if unchecked, result in blindness. For early detection and treatment, it is essential to comprehend the nature of these conditions and how they affect vision.
CAUSES OF BLURRY VISION
Refractive errors (nearsightedness, farsightedness, or astigmatism) or dry eyes are the most common causes of blurred vision, which is a lack of sharpness that makes it difficult to perceive fine details. It can affect one or both eyes and is frequently accompanied by halos, headaches, or eye strain. If blurring occurs suddenly, severely, or persistently, immediate medical intervention is necessary.
Types of Retinal Disorders;
Several types of retinal disorders can affect vision, including:
– Retinal Detachment:
This occurs when the pulls away from the underlying tissue, cutting off its blood supply and oxygen. This is a medical emergency that requires immediate attention to prevent permanent vision loss.
– Diabetic Retinopathy:
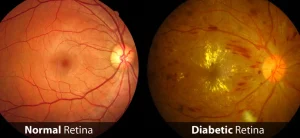
This condition develops in people with diabetes when high blood sugar levels damage the blood vessels in the retina, causing them to leak or bleed. It’s a leading cause of blindness in adults.
– Macular Degeneration:
Age-related macular degeneration (AMD) affects the macula, the central part of the retina, and leads to a loss of central vision. It’s more common in older adults and can make activities like reading and driving difficult.
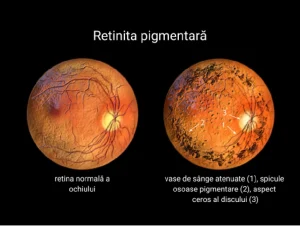
– Retinitis Pigmentosa:
CAUSES OF BLURRY VISION
This is a rare, inherited disorder that causes the gradual breakdown of retinal cells, leading to progressive vision loss over time.
Symptoms and Risk Factors;
Common symptoms of retinal disorders include blurred or distorted vision, floaters, flashes of light, and sudden vision loss. Risk factors may include aging, diabetes, family history, high blood pressure, and extreme nearsightedness (myopia).
Diagnosis and Treatment;

CAUSES OF BLURRY VISION
Retinal disorders are diagnosed through comprehensive eye exams and imaging tests such as optical coherence tomography (OCT) and fluorescein angiography. Treatments vary based on the disorder and may include medication, laser therapy, or surgery.
Prevention includes managing underlying health conditions like diabetes. Protecting the eyes from UV exposure, and regular eye exams to detect early changes.
Protecting your retina is essential for maintaining healthy vision, so don’t overlook the importance of regular check-ups and prompt medical attention.
Summary
Dry eyes, digital eye strain, cataracts, diabetic retinopathy, and uncorrected refractive defects (nearsightedness, farsightedness, and astigmatism) are the main causes of blurred vision, a frequent symptom with reasons ranging from moderate to serious. Serious, urgent crises including retinal detachment, stroke, or high blood pressure may be indicated by sudden, severe blurring.