
Technical and academic writing tips. Effective communication in each setting requires an understanding of the distinctions between academic and technical writing. Technical writing is on providing useful information in a clear, succinct, and user-friendly manner, whereas academic writing seeks to contribute to scholarly conversations through in-depth analysis and formal tone. By understanding these differences, writers can modify their style to suit the particular requirements of their target audience and goal.
TECHNICAL AND ACADEMIC WRITING TIPS
The main areas of distinction between academic and technical writing are style, audience, and goal. While academic writing concentrates on proving a theory or dissecting a subject for a scholarly audience, technical writing concentrates on teaching and clarity for a specific audience, hoping to assist them in completing a task.
1. Purpose and Audience;

• Academic Writing: Primarily aimed at contributing to scholarly discourse, academic writing seeks to inform, persuade, or explore theoretical concepts. Its audience includes students, researchers, and academicians who are often well-versed in the subject matter. Examples include research papers, theses, and literature reviews.
• Technical Writing: Focuses on conveying specific information clearly and concisely to help readers perform a task or understand a process. The audience can range from technical professionals to laypersons needing straightforward instructions. Examples include user manuals, technical reports, and instructional guides.
2. Structure and Organization;
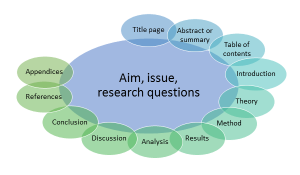
• Academic Writing: Typically follows a structured format, including an introduction, literature review, methodology, results, discussion, and conclusion. The organization emphasizes a logical flow of ideas, supporting arguments, and thorough analysis.
• Technical Writing: Uses a more flexible and practical structure, often including sections like introduction, background, procedure, and troubleshooting. The organization prioritizes clarity and ease of navigation, with headings, bullet points, and step-by-step instructions being common.
3. Style and Tone;

Technical and academic writing tips
• Academic Writing: Characterized by a formal, objective tone and a focus on critical analysis. The language is often complex, with the use of specialized terminology and citations from scholarly sources to support arguments.
• Technical Writing: Emphasizes simplicity and clarity, using straightforward language and avoiding unnecessary jargon. The tone is instructional and direct, aimed at making the information easily understandable and actionable.
4. Depth of Content;
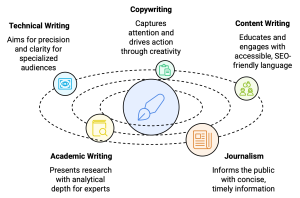
Technical and academic writing tips
• Academic Writing: Delves deeply into theoretical frameworks, extensive literature reviews, and comprehensive data analysis. It often involves presenting and defending hypotheses, exploring abstract concepts, and contributing new knowledge to the field.
• Technical Writing: Concentrates on practical information and specific details necessary for understanding or completing a task. It is more focused on functionality, providing concrete instructions and solutions without delving into theoretical backgrounds.
5. Use of Sources and Citations;

Technical and academic writing tips
• Academic Writing: Requires rigorous sourcing and citation of all referenced material, following specific academic styles (APA, MLA, Chicago, etc.). This practice ensures credibility, allows for peer review, and acknowledges the work of others in the field.
• Technical Writing: While it may include references to support information or provide context, it is generally less focused on extensive citations. The emphasis is on providing clear and concise information that users can apply directly, often with in-house or original sources.
Summary
Both academic and technical domains require effective communication, but the approach and manner might differ greatly based on the goal and target audience. Technical writing and academic writing are two different types of communication, each with its own standards and objectives.