Multiple system atrophy. Scientists are still investigating Multiple System Atrophy in an effort to better understand the underlying causes of the condition and create novel treatments. Clinical trials are investigating a number of strategies, such as drugs that may more effectively reduce symptoms or halt the course of the disease. Research developments give promise for better treatments and outcomes for people with MSA in the future, even though there is currently no known cure.
MULTIPLE SYSTEM ATROPHY
A uncommon and progressive neurological disease called Multiple System Atrophy (MSA) damages the body’s autonomic processes, which include things like blood pressure, heart rate, and digestion that we are not cognizant of. Because MSA resembles other neurodegenerative diseases like Parkinson’s disease, it can be difficult to diagnose. It is unique, though, in that it progresses quickly and exhibits a variety of symptoms.
Types;
Multiple System Atrophy
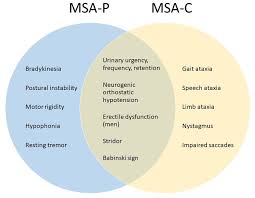
MSA is classified into two main types based on the predominant symptoms:
1. MSA-P (Parkinsonian Type): This type resembles Parkinson’s disease and is characterized by symptoms such as muscle rigidity, slow movement (bradykinesia), tremors, and balance difficulties.
2. MSA-C (Cerebellar Type): This type primarily affects the cerebellum, the part of the brain responsible for coordination. Symptoms include problems with balance, coordination, and speech (ataxia).
Causes and Risk Factors;
Multiple System Atrophy
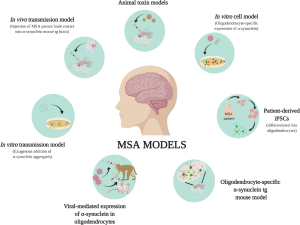
The exact cause of MSA is unknown, and no specific risk factors have been identified. Unlike many other neurodegenerative disorders, MSA is not inherited and does not have a known genetic link. The disease is thought to involve the accumulation of a protein called alpha-synuclein in certain areas of the brain, leading to cell damage and the symptoms of MSA.
Symptoms;
Multiple System Atrophy
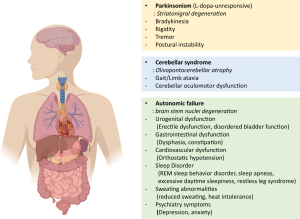
MSA symptoms vary widely depending on the type and progression of the disease but can include:
– Autonomic Dysfunction: This includes issues such as severe drops in blood pressure (orthostatic hypotension), urinary incontinence, erectile dysfunction, and difficulties with temperature regulation.
– Parkinsonism: Symptoms similar to Parkinson’s disease, such as stiffness, slow movements, and tremors.
– Cerebellar Ataxia: Problems with balance, coordination, and speech, leading to difficulty walking and performing tasks requiring fine motor skills.
– Sleep Disturbances: Many individuals with MSA experience sleep disorders like REM sleep behavior disorder, where they act out dreams.
Diagnosis;
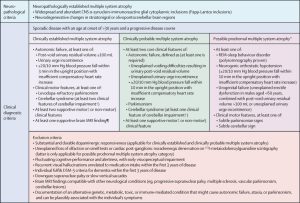
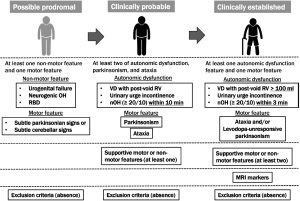
Diagnosing MSA can be challenging because its symptoms overlap with other conditions like Parkinson’s disease. Diagnosis typically involves a thorough clinical examination, patient history, and ruling out other conditions. Brain imaging, such as MRI, can help detect changes in the brain associated with MSA, but no specific test can definitively diagnose the condition.
Treatment and Management
Currently, there is no cure for MSA, and treatment focuses on managing symptoms to improve quality of life. Treatment options include:
– Medications: Drugs used to treat Parkinson’s disease may be prescribed to manage motor symptoms, though they are often less effective in MSA. Medications can also help control blood pressure, bladder function, and other autonomic symptoms.
– Physical Therapy: This can help maintain mobility, balance, and coordination, and occupational therapy can assist with daily activities.
– Supportive Care: Speech therapy, dietary changes, and assistive devices can help manage the various challenges posed by MSA.
– Lifestyle Modifications: Elevating the head during sleep, increasing fluid and salt intake, and using compression garments can help manage orthostatic hypotension.
Prognosis;
MSA is a progressive condition, and symptoms typically worsen over time. The rate of progression varies, but many individuals with MSA experience significant disability within a few years of diagnosis. The average life expectancy after diagnosis is 7 to 10 years, though this can vary depending on the individual’s overall health and how well symptoms are managed.
Summary
A thorough, multidisciplinary approach to treatment is necessary for Multiple System Atrophy, a complicated and crippling condition. Early diagnosis and proactive symptom management can greatly improve the quality of life for those with MSA, even though the prognosis might be challenging.