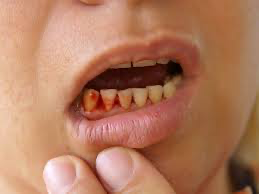
Bleeding from the teeth or gums is often a sign of an underlying dental issue. While occasional bleeding may not be serious, persistent or frequent bleeding should not be ignored, as it could indicate gum disease or other oral health problems.
Causes of Tooth Bleeding
Several factors can lead to bleeding teeth or gums:
– Gum Disease (Gingivitis or Periodontitis): Inflammation caused by plaque buildup can make gums swollen and prone to bleeding.
– Brushing Too Hard: Using a hard-bristled toothbrush or aggressive brushing can damage gums.
– Flossing Incorrectly: If not done gently, flossing can cause minor gum injuries.
– Vitamin Deficiencies: Lack of vitamin C or K can lead to gum bleeding.
– Tooth or Gum Infections: Bacterial infections can cause inflammation and bleeding.
– Hormonal Changes: Pregnancy or menopause can make gums more sensitive.
– Blood Disorders or Medications: Conditions like hemophilia or blood thinners can lead to excessive bleeding.
Prevention of Tooth Bleeding
To reduce the risk of bleeding teeth or gums, follow these oral hygiene practices:
– Brush Gently and Correctly: Use a soft-bristled toothbrush and brush in circular motions to avoid irritating the gums.
– Floss Daily: Floss gently to remove plaque without injuring the gums.
– Use an Antiseptic Mouthwash: Helps reduce bacteria and prevent infections.
– Eat a Balanced Diet: Ensure adequate intake of vitamin C (found in citrus fruits, peppers, and leafy greens) and vitamin K (found in spinach, kale, and broccoli).
– Stay Hydrated: Drinking water helps wash away bacteria and food particles.
– Quit Smoking: Smoking weakens the gums and increases the risk of gum disease.
– Visit the Dentist Regularly: Professional cleanings help remove plaque buildup and detect problems early.
Treatment for Tooth Bleeding
If bleeding persists, consider the following treatments:
1. Home Remedies
•Saltwater Rinse: Reduces inflammation and fights bacteria.
•Hydrogen Peroxide Rinse: Helps kill bacteria and promote healing.
•Aloe Vera Gel: Soothes and reduces gum inflammation.
2. Medical Treatments
•Professional Dental Cleaning: Removes plaque and tartar buildup.
•Scaling and Root Planing: Deep cleaning procedure for treating gum disease.
•Antibiotics or Antiseptic Gels: Used for severe infections.
•Surgical Treatments: In advanced cases of gum disease, gum grafting or laser therapy may be needed.
When to See a Dentist
Seek dental care if:
– Bleeding persists for more than a few days.
– Gums are swollen, red, or painful.
– There is a persistent bad taste or bad breath.
– Teeth feel loose or shifting.
Conclusion
Tooth bleeding is often caused by gum disease, poor oral hygiene, or vitamin deficiencies. Preventing it requires proper dental care, a healthy diet, and regular dental visits. If bleeding continues, consulting a dentist is essential to prevent serious complications.