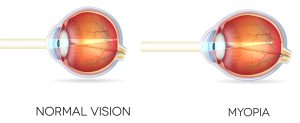
Reviewing shortsightedness. Myopia, often known as shortsightedness, is a common eye disorder in which light focuses in front of the retina rather than on it, making distant objects look hazy. The symptoms include headaches, squinting, eye strain, sitting near TVs or phones, and trouble seeing distant objects. It is frequently brought on by an excessively large eyeball or a sharply curved cornea. In order to delay the progression of myopia, particularly in youngsters, treatment options include glasses, contact lenses, and myopia management therapies including low-dose atropine eye drops or special multifocal contact lenses.
REVIEWING SHORTSIGHTEDNESS
Developing preventative and management measures for shortsightedness can be aided by an understanding of its complex causes. Myopia is caused by a combination of environmental variables, lifestyle choices, genetics, and eye strain. The dangers of shortsightedness can be reduced by promoting outdoor activities, taking regular breaks from close-up work, and keeping an eye on eye health. To identify and treat myopia early on, routine eye exams are very crucial. Here are five possible reasons for the development of shortsightedness:
1. Genetic Factors;

REVIEWING SHORTSIGHTEDNESS
Description:
Genetics play a significant role in the development of myopia. If one or both parents are shortsighted, there is a higher likelihood that their children will also develop myopia.
Evidence:
Studies have shown that the risk of myopia increases significantly if there is a family history of the condition. Research indicates that specific genes related to eye growth and development can influence the onset of myopia .
2. Environmental Factors and Lifestyle;
Description:
Prolonged near work activities, such as reading, writing, and using digital devices, can contribute to the development of myopia. Limited exposure to outdoor activities and natural light is also a factor.
Evidence:
Research has demonstrated a correlation between increased screen time and close-up work with higher rates of myopia, especially in children and adolescents. Outdoor activities, on the other hand, expose the eyes to natural light and help reduce the risk of myopia progression .
3. Excessive Eye Strain;

REVIEWING SHORTSIGHTEDNESS
Description:
Constantly straining the eyes to focus on nearby objects for extended periods can lead to myopia. This is particularly common in individuals who spend a lot of time reading or working on computers without taking breaks.
Evidence:
Eye strain can cause temporary myopia, which may become permanent if the strain is chronic and continuous. The “20-20-20 rule” (looking at something 20 feet away for 20 seconds every 20 minutes) is often recommended to reduce eye strain .
4. Lack of Adequate Outdoor Time;
Description:
Spending insufficient time outdoors has been linked to an increased risk of developing myopia. Natural light exposure is crucial for eye health.
Evidence:
Several studies suggest that children who spend more time outdoors have a lower incidence of myopia compared to those who spend more time indoors. Natural light is believed to help regulate eye growth and prevent excessive elongation of the eyeball, which causes myopia .
5. Abnormal Eye Growth;
REVIEWING SHORTSIGHTEDNESS
Description:
Myopia occurs when the eyeball grows too long, or the cornea is too curved, causing light entering the eye to focus incorrectly on the retina.
Evidence:
There are two possible causes of this aberrant growth: genetic and environmental. Although the precise processes are still being investigated, it is known that blurred distance vision results from images being focused in front of the retina rather than directly on it due to eyeball elongation.
Summary
Myopia, often known as shortsightedness, is a common visual impairment in which close items are plainly visible but distant objects appear hazy. Myopia can be prevented and managed with an understanding of its possible causes.