Venous insufficiency is a condition where the veins in the legs have difficulty sending blood back to the heart. This happens when the valves in the veins, which are supposed to keep blood flowing in one direction, become weak or damaged. As a result, blood pools in the veins, leading to a range of symptoms and complications.
Causes of Venous Insufficiencies
1. Valve Dysfunction: The most common cause of venous insufficiency is the failure of valves within the veins. These valves normally close after blood passes through, preventing it from flowing backward. When they don’t function properly, blood can accumulate in the legs.
2. Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT): A blood clot in a deep vein, often in the leg, can damage the valves, leading to chronic venous insufficiency.
3. Age and Genetics: As people age, their veins and valves may naturally weaken, increasing the risk of venous insufficiency. Genetics also plays a role, with a family history of the condition raising the likelihood of developing it.
4. Prolonged Standing or Sitting: Occupations that require long periods of standing or sitting can contribute to venous insufficiency, as they hinder proper blood flow in the legs.

5. Obesity and Pregnancy: Excess weight puts additional pressure on the veins, increasing the risk of valve dysfunction. Pregnancy also adds pressure to the veins in the pelvis and legs, potentially leading to venous insufficiency.
Symptoms of Venous Insufficiency
The symptoms of venous insufficiency can vary in severity and may include:
– Swelling in the Legs and Ankles: This is often one of the earliest signs, caused by the buildup of blood in the lower limbs.
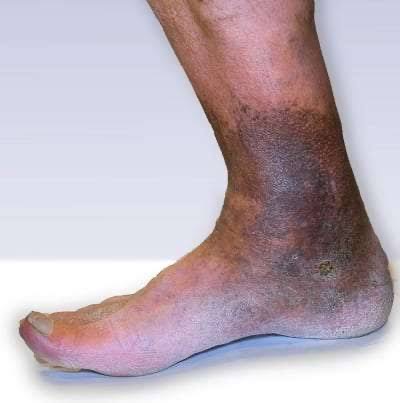
– Varicose Veins: These are enlarged, twisted veins that are often visible under the skin. They can be painful and unsightly.
– Pain or Aching in the Legs: This discomfort is usually worse after prolonged periods of standing or sitting and may improve with leg elevation.
– Skin Changes: The skin on the legs may become dry, itchy, or discolored (often brownish). In severe cases, ulcers can develop, particularly around the ankles.
– Heaviness or Fatigue in the Legs: The legs may feel heavy, tired, or restless, especially at the end of the day.
Treatment of Venous Insufficiency
Managing venous insufficiency focuses on improving blood flow and alleviating symptoms. Common treatments include:
1. Compression Stockings: These specialized stockings apply pressure to the legs, helping veins push blood back toward the heart. They are often the first line of treatment.
2. Lifestyle Changes: Regular exercise, weight management, and avoiding prolonged periods of standing or sitting can improve circulation. Elevating the legs whenever possible also helps reduce swelling.
3. Medications: In some cases, medications that improve blood flow or reduce pain and inflammation may be prescribed.
4. Minimally Invasive Procedures: If conservative treatments are not effective, procedures like sclerotherapy (injecting a solution into the vein to close it) or endovenous laser therapy (using a laser to close the vein) may be recommended.
5. Surgery: In severe cases, surgery may be necessary to remove or repair damaged veins.
Venous insufficiency is a common but manageable condition that affects many people, particularly as they age. Early recognition and treatment are key to preventing complications and improving quality of life. If you experience symptoms of venous insufficiency, it’s important to seek medical advice to explore the best treatment options for your situation. With the right care, most people can effectively manage the condition and avoid serious complications.