Neurological conditions encompass a broad range of disorders affecting the brain, spinal cord, and nerves. These conditions can impact various aspects of bodily functions, including movement, sensation, cognition, and autonomic processes. Understanding these conditions is crucial for effective diagnosis, treatment, and management.
Types of Neurological Conditions
1. Stroke: A stroke occurs when blood flow to a part of the brain is interrupted, leading to brain cell damage. This can result in sudden loss of abilities such as speech, movement, or cognition, depending on the affected brain region.
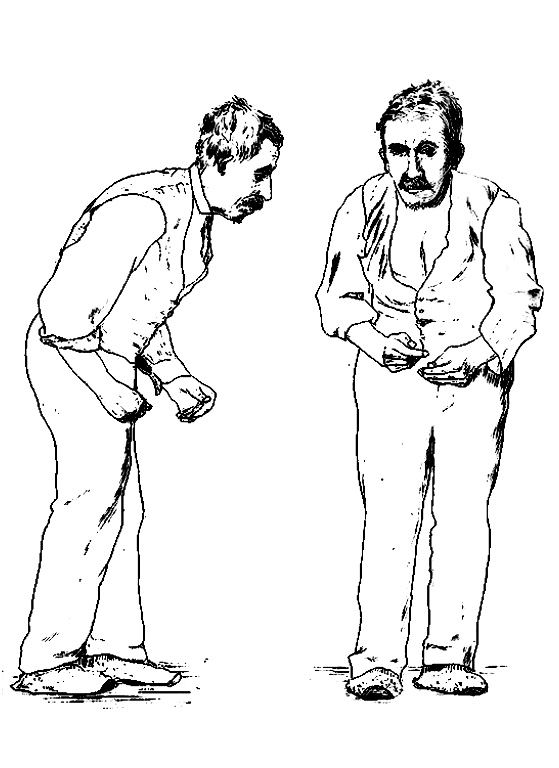
2. Parkinson’s Disease: Parkinson’s disease is a progressive disorder characterized by tremors, rigidity, and bradykinesia (slowness of movement). It results from the degeneration of dopamine-producing neurons in the brain.
Screenshot
3. Multiple Sclerosis (MS): MS is an autoimmune condition where the immune system attacks the protective covering of nerve fibers, leading to a wide range of symptoms including muscle weakness, vision problems, and difficulty with coordination.

4. Alzheimer’s Disease: Alzheimer’s disease is a progressive neurodegenerative disorder that causes memory loss, cognitive decline, and changes in behavior. It is the most common form of dementia.

5. Epilepsy: Epilepsy is characterized by recurrent seizures caused by abnormal electrical activity in the brain. Seizures can vary from brief lapses in awareness to intense convulsions.

6. Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis (ALS): ALS, also known as Lou Gehrig’s disease, is a progressive neurodegenerative disease that affects motor neurons, leading to muscle weakness, paralysis, and ultimately, respiratory failure.
Symptoms and Diagnosis
Neurological conditions present a diverse array of symptoms, including but not limited to:
– Motor Symptoms: Such as tremors, muscle weakness, or loss of coordination.
– Cognitive Symptoms: Including memory loss, difficulty concentrating, or impaired judgment.
– Sensory Symptoms: Like numbness, tingling, or altered sensations.
– Autonomic Symptoms: Affecting involuntary functions such as blood pressure regulation or digestion.
Diagnosing neurological conditions often involves a combination of medical history, physical examinations, and advanced diagnostic tools such as MRI, CT scans, and electroencephalograms (EEGs).
Treatment and Management
Treatment for neurological conditions varies depending on the specific disorder but may include:
– Medications: To manage symptoms or slow disease progression.
– Physical Therapy: To improve movement, coordination, and strength.
– Occupational Therapy: To assist with daily activities and improve quality of life.
– Surgical Interventions: In some cases, surgery may be necessary to address specific issues or alleviate symptoms.
Supportive care, including counseling and lifestyle modifications, is also important for managing the impact of neurological conditions on daily life.
In summary, neurological conditions are complex and varied, affecting numerous aspects of health and well-being. Early diagnosis and a multidisciplinary approach to treatment can significantly improve outcomes and quality of life for individuals affected by these disorders.