PREVENTION OF EAR DRUMS DISORDER
Prevention of ear drums disorder. Both bacterial and viral illnesses can cause ear infections. They can happen in the outer and inner ears, as well as the middle ear, which is the area of the ear directly behind the eardrum. Although they frequently go away on their own, swelling or fluid accumulation can make them painful and amount to earing loss.
PREVENTION OF EAR DRUMS DISORDER
Both acute and persistent ear infections are possible. Although they hurt, acute ear infections don’t last long. Ear infections that are chronic either don’t go away or keep coming back. They may result in middle and inner ear damage, which is rarely irreversible.
Symptoms of ear disorder
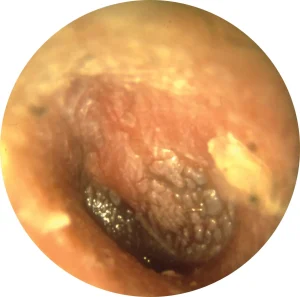
Young toddlers and babies may exhibit additional symptoms of an Ear infections in addition to the symptoms common in adults, such as ear pain and drainage: • scratching or pulling their ear; • fever; • not reacting to particular sounds; • constantly losing their balance • headache; • irritability or restlessness; bleeding.• appetite loss Ear infections often go away in less than three days, although they can linger for up to a week.
Treatment

Although the majority of minor ear infections resolve on their own, the following therapies may potentially be beneficial: Treatment at home The following techniques work well for reducing the signs of a minor ear infection:
• Place a warm cloth over the ear that is afflicted. Take painkillers that are available over-the-counter.
• To ease pain, apply over-the-counter or prescription ear drops. Decongestants such as pseudoephedrine (Sudafed) are available over-the-counter.
• Do not sleep on the ear that is afflicted.
Medical treatment
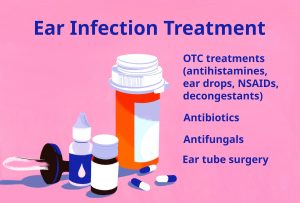
Consult a physician if your symptoms worsen or remain the same. If your ear infection is bacterial, persistent, or doesn’t seem to be getting better, they might recommend medications. Viral infections cannot be treated with antibiotics. Operation If the standard conventional therapies don’t clear up your ear infection or if you get ear infections frequently in a short period of time, surgery might be your best bet. Ear tubes are typically inserted into your ears to let fluid escape. Your eardrums are surgically opened to accommodate these tubes. The holes eventually heal once they fall out. Occasionally, surgery is required to seal these gaps.
Prevention
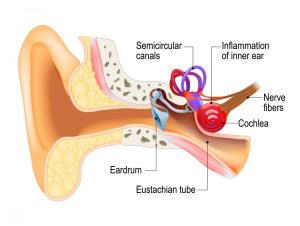
A ruptured eardrum can be avoided in large part by protecting your ears. Here are some tips for safeguarding your ears and eardrum:
• Receiving therapy for infections in the middle ear: Earache, nasal congestion, fever, and hearing problems are all signs of a middle ear infection. If your symptoms persist for more than a few days, get in touch with a medical professional.
• Cleaning carefully: Avoid cleaning your ears with cotton swabs or other things because they can easily burst an eardrum. Rather, use a clean finger or the end of a clean cloth to gently wipe the outside of your ear.
Summary
The eardrum is a delicate organ. It is also a necessary tool. Your hearing and balance may be impacted by an eardrum rupture. Because your damaged eardrum is unable to shield your middle ear from microorganisms that invade it, it may also make you more susceptible to ear infections. Your eardrum has to be protected because of this.