
Causes of leukoplakia. The disorder known as leukoplakia results in the development of painless white or gray patches inside the mouth. Something that irritates the inside of your mouth may cause leukoplakia. Leukoplakia patients may be more susceptible to oral cancer. Medical professionals operate to remove the patches in order to address the ailment.
CAUSES OF LEUKOPLAKIA
A disorder called leukoplakia causes white spots to appear in your mouth. Even when you rub the patches, they remain in place even though they don’t hurt. Something that irritates the inside of your mouth may cause leukoplakia. Because leukoplakia can develop into oral cancer, , your dentist could advise you to consult a specialist for diagnosis and treatment.
Types

When homogeneous leukoplakia occurs, it may seem as a flat, white spot in your mouth. The patch’s surface could be ridged, wrinkled, or smooth. Since this leukoplakia is usually benign, mouth cancer seldom develops from it. Compared to non-homogeneous leukoplakia, it is more prevalent.
non-homogeneous leukoplakia: This condition might result in irregular or strangely shaped red or white patches in your mouth. The areas could have elevated surfaces or be flat. Research indicates that the likelihood of non-homogeneous leukoplakia developing into cancer is seven times higher than that of homogenous leukoplakia.
Signs
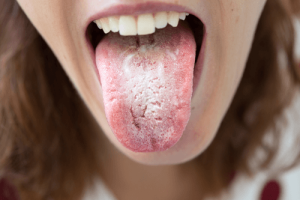
Patches that remain inside your mouth are a sign of leukoplakia. The patches could show up on the inside of your cheeks, gums, or tongue.
Appear flat or slightly elevated.
be gray, white, or white with small red spots.
Causes
If something irritates the tissue lining the inside of your mouth, leukoplakia may occur. You might, for instance, employ poorly fitting dentures or eat the inside of your cheeks.
Leukoplakia can also occur as a result of gene mutations. (Genes instruct cells on how to divide, how quickly to proliferate, and when to die off to make place for new cells.) Genetic abnormalities in leukoplakia cause cells in the oral tissue to proliferate more quickly than they should, resulting in patches.
Treatment

Medical professionals remove the patches in your mouth to cure leukoplakia. They might use a scalpel to cut out the patches. Other possible processes consist of:
removing the patches with a laser.
using photodynamic therapy, or light-activated cancer medications.
using cryotherapy, a freezing process that eliminates aberrant cells and eliminates the patches.
removing the patches with an electrically heated needle or other tool.
Prevention

Leukoplakia may not be preventable because experts aren’t always certain what causes it. Leukoplakia, however, is associated with alcohol and tobacco usage. You could reduce your risk by:
avoiding tobacco products, such as smokeless and chewing tobacco.
consuming less alcoholic beverages overall. Those who choose to consume alcoholic beverages should limit their consumption to no more than two drinks per day for men and one drink per day for women, advises the American Cancer Society.
Summary
A disorder called leukoplakia causes white spots to appear on your tongue, gums, or the inside of your cheeks. Although the patches don’t hurt, they remain. Despite its seemingly innocuous appearance, leukoplakia can develop into mouth cancer. Any white areas in your mouth should be discussed with your dentist. They will check your mouth and, if necessary, send you to other experts for examinations and care.