
DANDELIONS
Dandelions. Overnight, dandelions appear to overshadow your flower garden’s petunias and mar a perfectly manicured grass. However, you might want to invite the omnipresent yellow weeds into your kitchen rather than fighting them. When included in a well-balanced diet and supplement program, dandelion may have several health benefits for people. Before adding it to their diet, consumers should see a physician, as is the case with any dietary or supplement modifications.
DANDELIONS
For ages, dandelion has been utilized in traditional medicine, despite being frequently written off as a difficult lawn weed. In addition to adding color to your dish, the leaves, roots, and blossoms are frequently used in herbal teas and supplements.
1. incredibly nourishing

Dandelions are incredibly nutrient-dense plants that are rich in fiber, vitamins, and minerals from root to blossom.
Vitamins A, C, and K are abundant in dandelion greens, which can be either fresh or cooked. They also have trace levels of other B vitamins, vitamin E, and folate. Among the minerals found in dandelion greens are potassium, magnesium, calcium, and iron. The carbohydrate inulin, a form of soluble fiber present in plants and abundant in dandelion root, promotes the development and upkeep of beneficial gut flora in your digestive system.
2. have strong antioxidants

Strong Antioxidants found in dandelion may account for many of its therapeutic benefits. Antioxidants are substances that aid in the neutralization of free radical molecules, which are produced by your metabolism but raise your chance of developing chronic diseases if they build up too much in your body. Antioxidants are therefore essential for your general well-being. High concentrations of the antioxidant beta-carotene found in dandelion may offer protection against oxidative stress and cell damage.
3. assist in reducing inflammation
Compounds like polyphenols in dandelion may help lower Inflammation. The immune system’s natural reaction to damage or infection is inflammation. On the other hand, chronic inflammation can harm DNA and bodily tissues irreversibly.
4. assist in controlling blood sugar levels
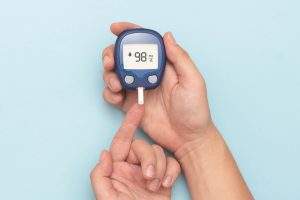
Dandelion flowers, leaves, and roots include two bioactive substances that may help lower blood sugar levels: chicoric and chlorogenic acids. In addition to limiting the digestion of starchy, high-carb meals, chicoric and chlorogenic acid may also help to reduce blood sugar levels.
5. lower triglyceride and cholesterol levels
Certain substances included in dandelion’s roots, leaves, seeds, and flowers may lower cholesterol and triglyceride levels, two major heart disease risk factors. Flavonoids and derivatives of hydroxycinnamic acid are types of polyphenols found in dandelion that may have the ability to reduce triglycerides and cholesterol.
6. Reduce the blood pressure
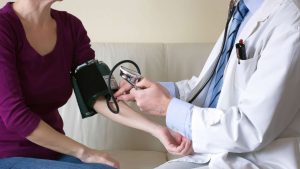
Studies are scarce, despite some people’s claims that dandelion leaf extracts can lower blood pressure. To assist lower blood pressure, diuretic drugs are used in Western medicine to help the body get rid of extra fluid.
Summary
Even with all of their potential advantages, dandelion plants and supplements shouldn’t be used in place of a healthy diet and way of life. There is a dearth of research on particular uses, particularly in people. This root vegetable is a distinctive and nutrient-dense addition to your diet if you eat its greens, roots, and blooms in their entirety in salads, baked goods, sides, and snacks.