Difficulty in swallowing. Identifying and treating dysphagia early on can improve swallowing function and improve quality of life for those who suffer from it. Accurate diagnosis and appropriate management of swallowing difficulties depend on understanding the different factors that can cause them. Treatment options may include medication, surgery, lifestyle changes, dietary changes, swallowing therapy, or other treatments, depending on the underlying cause.
DIFFICULTY IN SWALLOWING
Dysphagia, another name for swallowing difficulties, can affect people of all ages and arise for a variety of causes. From minor pain to severe impairment, dysphagia affects a person’s ability to swallow, eat, and drink safely. For an accurate diagnosis and successful treatment, it is essential to comprehend the common reasons of swallowing difficulties.
1. Neurological Conditions:

DIFFICULTY IN SWALLOWING
Neurological disorders affecting the brain or nerves involved in swallowing can lead to dysphagia. Conditions such as stroke, Parkinson’s disease, multiple sclerosis, amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS), and dementia can impair the coordination of swallowing muscles and disrupt the swallowing reflex.
2. Structural Abnormalities:
Structural abnormalities or anatomical defects in the mouth, throat, or esophagus can cause swallowing difficulties. Examples include cleft palate, enlarged tonsils or adenoids, tumors or growths in the throat or esophagus, and narrowing of the esophagus (esophageal stricture).
3. Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease:
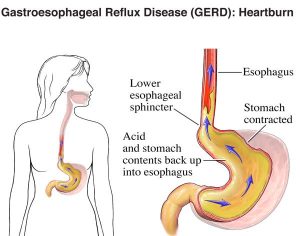
DIFFICULTY IN SWALLOWING
GERD is a digestive disorder characterized by the backflow of stomach acid into the esophagus, causing irritation and inflammation of the esophageal lining. Chronic GERD can lead to esophageal narrowing, scarring, and difficulty swallowing (dysphagia).
4. Muscle Weakness or Dysfunction:
Weakness or dysfunction of the muscles involved in swallowing (such as the tongue, throat, and esophagus) can result in dysphagia. Muscle weakness may be caused by conditions such as myasthenia gravis, muscular dystrophy, or aging-related muscle loss (sarcopenia).
5. Esophageal Motility Disorders:
DIFFICULTY IN SWALLOWING
Disorders that affect the motility or movement of the esophagus can cause swallowing difficulties. Examples include achalasia (a condition characterized by impaired esophageal muscle relaxation) and esophageal spasm (abnormal contractions of the esophageal muscles).
6. Side Effects of Medications:
Certain medications, particularly those that affect muscle function or cause dry mouth, can contribute to swallowing difficulties. Examples include muscle relaxants, anticholinergic drugs, and medications used to treat psychiatric disorders.
7. Radiation Therapy and Surgery:
Radiation therapy and surgical procedures involving the head, neck, or chest can cause scarring, inflammation, or damage to the structures involved in swallowing, leading to dysphagia as a side effect of treatment.
8. Psychological Factors:
Psychological factors such as anxiety, depression, or fear of choking can also contribute to swallowing difficulties, particularly in individuals with psychogenic dysphagia.
9. Age-Related Changes:

Aging is associated with changes in swallowing function, including decreased muscle strength and coordination, reduced saliva production, and changes in the structure of the throat and esophagus. These age-related changes can contribute to swallowing difficulties in older adults.
10. Dental Problems:
Dental issues such as missing teeth, ill-fitting dentures, or oral infections can affect chewing and swallowing, leading to dysphagia. Poor dental hygiene and untreated dental problems can exacerbate swallowing difficulties.
14. Trauma or Injury:
Trauma or injury to the head, neck, or chest can damage structures involved in swallowing, leading to temporary or permanent dysphagia. Traumatic brain injury, spinal cord injury, or injuries resulting from accidents or surgery may affect swallowing function.
16. Poor Eating Habits:

Poor eating habits, such as eating too quickly, not chewing food thoroughly, or swallowing large pieces of food, can increase the risk of choking and contribute to dysphagia. Encouraging mindful eating practices and proper chewing techniques can help prevent swallowing difficulties.
Summary
Dehydration or malnutrition can impair general health and weaken the swallowing muscles, which might result in dysphagia. Sufficient hydration and nourishment are necessary to preserve the best possible swallowing function and avoid problems.