Heart failure early signs. A variety of symptoms and possible complications result from heart failure, which is caused by the heart’s inability to pump blood efficiently. For the condition to be managed and results to be improved, early detection is essential. Early detection of heart failure symptoms can help with prompt medical intervention and therapy. For a timely diagnosis and efficient treatment, it is crucial to identify the early indicators of heart failure, which include shortness of breath, exhaustion, swelling, coughing, irregular heartbeat, and weight gain. For people with heart failure, prompt intervention can greatly enhance their quality of life and health outcomes.
HEART FAILURE EARLY SIGNS
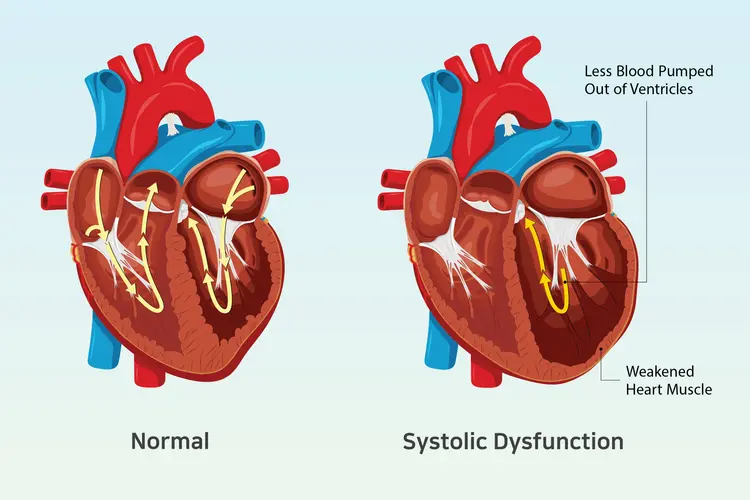
Heart failure is a chronic illness in which the heart muscle is unable to pump enough blood to meet the body’s oxygen needs. As a result, blood backs up in the body and lungs, causing symptoms like weariness, shortness of breath, and leg edema. Although not a quick fix, it’s a dangerous state brought on by diseases like high blood pressure or coronary artery disease that is frequently treated with drugs, gadgets, lifestyle modifications, and even surgery in an effort to reduce symptoms and enhance quality of life.
Common Early Signs;

1. Shortness of Breath:
One of the most common early symptoms is shortness of breath, which may occur during physical activity or even while at rest. This is due to fluid buildup in the lungs (pulmonary congestion) and reduced efficiency of the heart’s pumping action.
2. Fatigue and Weakness:
Individuals with early heart failure often experience unusual fatigue and weakness. This occurs because the heart’s reduced capacity to pump blood efficiently leads to decreased oxygen and nutrient delivery to tissues and muscles.
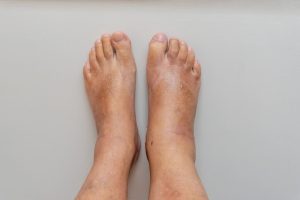
3. Swelling in the Extremities:
HEART FAILURE EARLY SIGNS
Swelling, or edema, in the legs, ankles, or feet can be an early sign of heart failure. Fluid accumulation occurs when the heart’s reduced pumping ability causes fluid to build up in the lower extremities.
4. Persistent Cough or Wheezing:
A chronic cough or wheezing, especially when lying down, may be indicative of fluid accumulation in the lungs. This symptom often worsens at night and can be mistaken for other respiratory conditions.
5. Rapid or Irregular Heartbeat:

HEART FAILURE EARLY SIGNS
An early sign of heart failure can be a noticeable increase in heart rate or irregular heartbeats. This occurs as the heart struggles to maintain adequate circulation and compensates for its reduced pumping efficiency.
6. Unexplained Weight Gain:
Sudden or unexplained weight gain, particularly if it is rapid, can result from fluid retention. Monitoring weight changes can help identify early fluid buildup associated with heart failure.
Importance of Early Detection;
HEART FAILURE EARLY SIGNS
Early recognition of these symptoms allows for timely medical evaluation and intervention. If heart failure is suspected, a healthcare provider may perform diagnostic tests such as blood tests, echocardiograms, or chest X-rays to confirm the diagnosis and determine the appropriate treatment plan.
Treatment;
Managing heart failure typically involves lifestyle changes, medications, and sometimes medical procedures. Treatments aim to reduce symptoms, improve heart function, and address the underlying causes of the condition. Key aspects of management include:
– Medications: To help reduce fluid buildup, improve heart function, and manage symptoms.
– Lifestyle Changes: Such as reducing salt intake, monitoring fluid intake, and engaging in regular physical activity.
– Regular Monitoring: To track symptoms and adjust treatment as needed.
Summary
Fatigue, shortness of breath (particularly when lying down or engaging in physical activity), edema in the legs, ankles, and feet, rapid weight gain from fluid, and a persistent cough are common early indicators of heart failure because the heart’s inability to pump enough blood results in fluid backup and decreased oxygen delivery. Other symptoms include a fast or erratic heartbeat, trouble exercising, and occasionally cognitive problems including disorientation.