The nails on your hands are not only important for everyday tasks but also serve as a reflection of your overall health. However, they can become susceptible to various infections, which can cause discomfort, pain, and cosmetic issues. These infections are typically caused by bacteria, fungi, or viruses and can range from mild to severe. Understanding these infections, their causes, and how to treat them is key to maintaining healthy nails.
1. Fungal Infections (Onychomycosis)
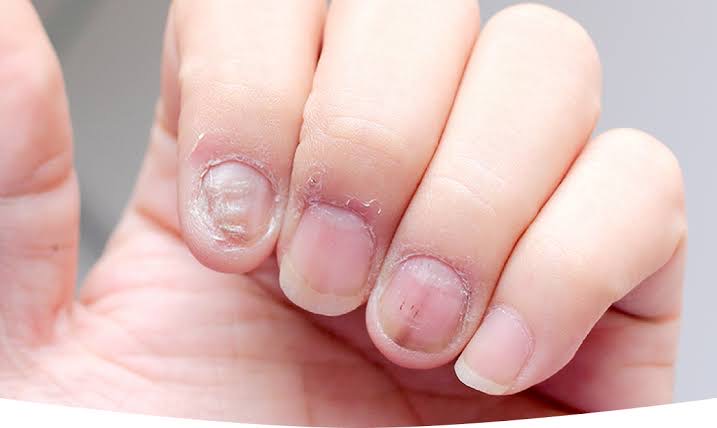
Fungal infections, particularly onychomycosis, are one of the most common types of infections that affect nails. These infections typically affect the toenails but can also affect the fingernails.
– Causes: Fungi like Trichophyton and Candida thrive in warm, damp environments. Nail trauma, poor hygiene, or contact with infected surfaces can introduce these fungi to the nails.
– Symptoms: Thickened nails, discoloration (yellow, white, or brown), crumbling at the edges, and a foul smell.
– Treatment: Antifungal medications, either topical (applied directly to the nail) or oral (prescribed by a doctor), are often used to treat fungal nail infections. In severe cases, the affected nail may need to be removed.
Paronychia is a bacterial infection that affects the skin around the nails, usually caused by bacteria entering through cuts, hangnails, or damaged skin.
– Causes: Most commonly caused by Staphylococcus aureus or Streptococcus bacteria. It can occur after a manicure, nail biting, or injury to the skin near the nail.
– Symptoms: Redness, swelling, pain, and pus around the nail. The area may be warm to the touch.
– Treatment: Mild cases can be treated with over-the-counter antibiotic ointments. In more severe cases, oral antibiotics or drainage of pus may be required. Keeping the area clean and dry can help prevent the infection from worsening.
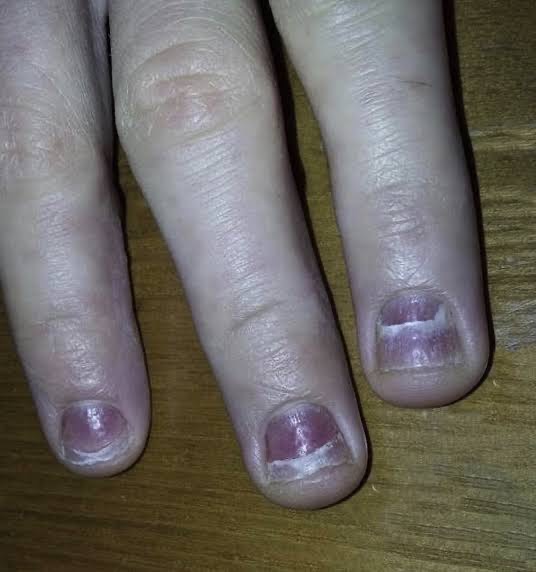
Warts that appear on or around the nails are caused by the human papillomavirus (HPV), which leads to the growth of benign, fleshy lumps on the skin.
– Causes: HPV is contracted through direct contact with infected skin or surfaces, such as public pools or shared nail care tools.
– Symptoms: Small, raised bumps around the nail, often with a rough surface. These warts may be painful, especially when pressure is applied.
– Treatment: Topical treatments like salicylic acid, cryotherapy (freezing the wart), or laser therapy may be used to remove the warts. In severe cases, surgical removal may be necessary.
4. Ingrown Nails (Onychocryptosis)
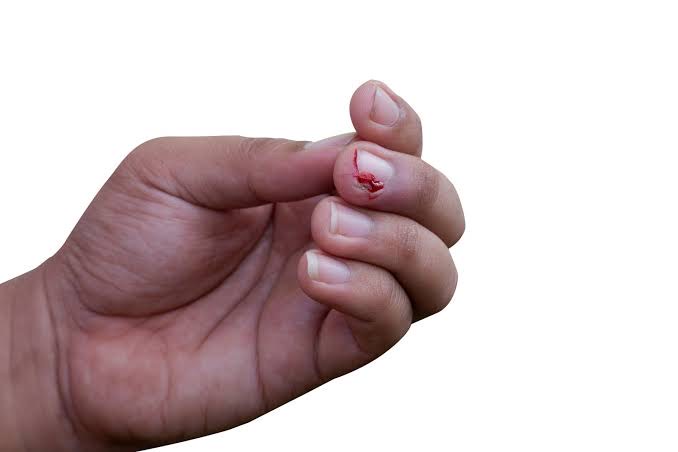
An ingrown nail occurs when the edge of the nail grows into the surrounding skin, often causing infection.
– Causes: Tight footwear, improper nail trimming, or trauma to the nail can cause the nail to grow incorrectly, becoming embedded in the skin.
– Symptoms: Pain, redness, swelling, and sometimes pus around the nail, usually in the big toe but also affecting finger nails.
– Treatment: Soaking the affected area in warm water, proper nail trimming, and wearing comfortable shoes. In more severe cases, a doctor may need to surgically remove part of the nail.
5. Nail Bed Infections (Onycholysis)
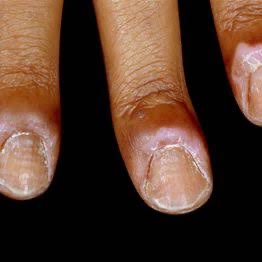
Onycholysis is the separation of the nail from the nail bed, which can occur due to a bacterial or fungal infection.
– Causes: Nail trauma, excessive moisture, or underlying health conditions like psoriasis can cause this condition. Bacteria or fungi can infect the exposed nail bed.
– Symptoms: Separation of the nail from the bed, discoloration (often white or yellow), and sometimes pain or discomfort.
– Treatment: Treatment depends on the underlying cause. Fungal infections may require antifungal treatment, while bacterial infections may need antibiotics.
6. Candida Infections
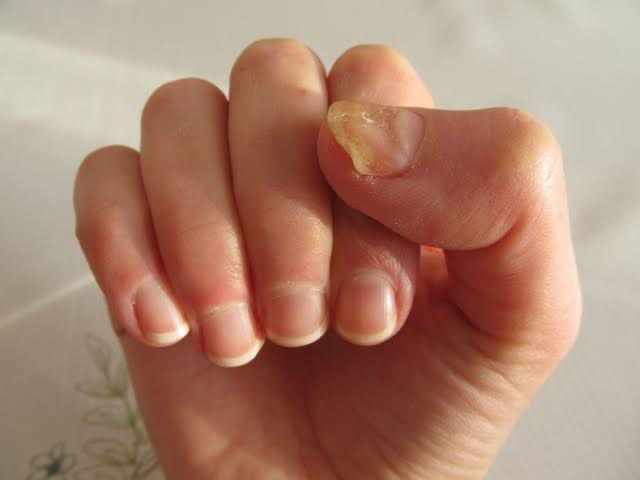
Candida, a type of yeast, can infect the nails, particularly the cuticles, and is often a result of excessive moisture or compromised immune systems.
– Causes: Prolonged exposure to water or a weakened immune system increases the risk of a Candida infection.
– Symptoms: Redness, swelling, and pus around the nails, often accompanied by a whitish discoloration of the nail.
– Treatment: Antifungal treatments, either topical or oral, can help clear up the infection. Maintaining good hand hygiene and keeping nails dry are also important.
Prevention Tips for Nail Infections
– Maintain Hygiene: Wash your hands and nails regularly with soap and water. Keep your nails dry and trimmed to avoid fungal or bacterial growth.
– Avoid Nail Biting: Biting your nails can introduce bacteria and fungi, leading to infections.
– Wear Proper Footwear: If you have fungal infections in your toenails, wear breathable, moisture-wicking socks and shoes.
– Use Clean Nail Tools: Disinfect manicure tools before use, especially if they have been in contact with someone else’s nails.
– Protect Your Nails: Wear gloves when handling chemicals or doing dishes to prevent trauma to the nails or exposure to harmful substances.
Conclusion
Hand nail infections can range from mild cosmetic issues to serious health problems. Fungal, bacterial, viral, and other types of infections can cause discomfort, discoloration, and damage to the nails. Identifying the cause of the infection early and seeking appropriate treatment is essential to prevent further complications. By practicing good nail care and hygiene, many infections can be prevented, ensuring your nails stay healthy and strong.