Malaria is a life-threatening disease caused by Plasmodium parasites, transmitted to humans through the bites of infected female Anopheles mosquitoes. Despite significant global efforts to control and eradicate malaria, it remains a major public health challenge in many parts of the world, particularly in sub-Saharan Africa.
Transmission of malaria
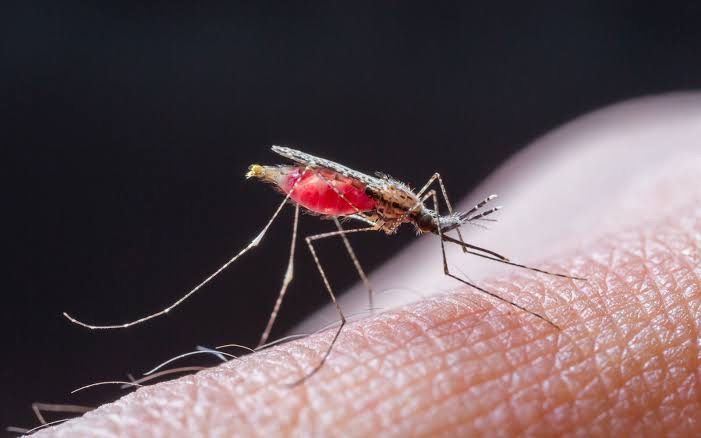
Malaria is transmitted by the bite of an infected Anopheles mosquito. The mosquito injects Plasmodium parasites into the bloodstream, where they travel to the liver, mature, and then re-enter the bloodstream to infect red blood cells. There are five species of Plasmodium that can infect humans, with Plasmodium falciparum being the most deadly.
Symptoms of malaria
Symptoms of malaria typically appear 10 to 15 days after the infected mosquito bite. They can include:
– Fever: High, recurring fevers are a hallmark of malaria.
– Chills: Intense chills and shivering often accompany fever episodes.
– Headache: Severe headaches are common.
• Muscle and Joint Pain: Muscle aches and joint pain are frequent symptoms.
– Fatigue: Profound fatigue and general malaise.
– Nausea and Vomiting: Gastrointestinal symptoms may occur.
• Sweating: Profuse sweating often follows fever episodes.
In severe cases, malaria can cause complications such as anemia, respiratory distress, organ failure, and cerebral malaria, which affects the brain and can be fatal if not treated promptly.
Prevention
Preventing malaria involves a combination of measures to avoid mosquito bites and control mosquito populations. Key preventive strategies include:
– Use Insect Repellents: Apply repellents containing DEET, picaridin, or oil of lemon eucalyptus to exposed skin.
– Sleep Under Mosquito Nets: Use insecticide-treated mosquito nets (ITNs) when sleeping, particularly in areas with high malaria transmission.
– Wear Protective Clothing: Wear long-sleeved shirts, long pants, and socks to reduce skin exposure.
– Indoor Residual Spraying (IRS): Spraying the interior walls of homes with insecticides can help reduce mosquito populations.
– Eliminate Standing Water: Remove or manage standing water where mosquitoes breed, such as in containers, puddles, and stagnant ponds.
– Antimalarial Medications: For travelers to malaria-endemic areas, taking prophylactic antimalarial drugs can reduce the risk of infection. Consult a healthcare provider for recommendations based on travel destination.
Treatment
Prompt treatment is crucial for malaria, especially for infections caused by Plasmodium falciparum. Treatment typically involves antimalarial medications, such as:
– Artemisinin-based Combination Therapies (ACTs): These are the most effective treatment for P. falciparum malaria.
– Chloroquine: Used for infections caused by P. vivax, P. ovale, P. malariae, and some strains of P. falciparum in regions where resistance to chloroquine is not a concern.
– Other Medications: Depending on the specific parasite species and resistance patterns, other drugs like mefloquine, quinine, or primaquine may be used.
Malarias remains a significant global health challenge, particularly in tropical and subtropical regions. Understanding the symptoms, modes of transmission, and preventive measures is essential for reducing the risk of infection and managing the disease effectively. Through continued efforts in mosquito control, the use of insecticide-treated nets, preventive medications, and public health initiatives, progress can be made towards reducing the burden of malarias and ultimately achieving its eradication.

Pingback: Five Sicknesses Neem Tree Leaves Can Help Cure - SimplExplainer