
Throat pains. A number of things, from simple irritations to more serious diseases or disorders, can produce throat aches. Determining the best course of treatment for throat discomfort requires an understanding of its underlying etiology. Even while self-care and home remedies can frequently help, severe or ongoing symptoms should always be evaluated and treated by a healthcare provider.
THROAT PAIN
Despite being frequent, throat pain can be very bothersome and interfere with day-to-day activities. Knowing the origins, symptoms, and available treatments for throat pain is crucial for controlling and reducing discomfort, whether it be from small irritations or more serious problems.
Causes of Throat Pain:
1. Viral Infections:
The most frequent cause of throat pain is viral infections, such as the common cold or flu. These infections can lead to inflammation and soreness in the throat.
2. Bacterial Infections:
Streptococcal bacteria, which cause strep throat, are another common culprit of throat pain. Strep throat often presents with severe pain, difficulty swallowing, and fever.
3. Allergies:
Allergic reactions to environmental irritants like pollen, dust, or pet dander can cause throat irritation and discomfort.
4. Acid Reflux:
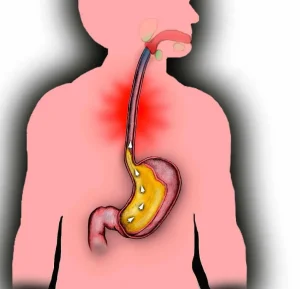
Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) can lead to stomach acid flowing back into the esophagus, causing irritation and soreness in the throat.
5. Smoking:
Smoking cigarettes or exposure to secondhand smoke can irritate the throat lining, leading to chronic throat pain.
6. Dry Air:
Breathing dry air, especially in heated or air-conditioned environments, can dry out the throat and cause irritation.
7. Strain:

Overuse of the vocal cords, such as excessive talking, yelling, or singing, can strain the throat muscles and lead to pain.
Symptoms of Throat Pain:
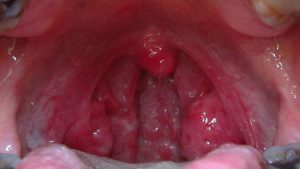
– Soreness: The most common symptom is a persistent soreness or discomfort in the throat.
– Difficulty Swallowing: Pain or difficulty when swallowing liquids or solids.
– Hoarseness: Changes in voice tone or quality due to inflammation or irritation.
– Swollen Glands: Swelling of the lymph nodes in the neck, indicating an immune response to infection.
– Fever: Infections may be accompanied by fever, especially in cases of bacterial origin.
Treatment Options:

throat pain
1. Rest and Hydration: Adequate rest and hydration are essential for the body to fight off infections and promote healing.
2. Pain Relief: Over-the-counter pain relievers such as ibuprofen or acetaminophen can help alleviate throat discomfort and reduce inflammation.
3. Throat Lozenges and Sprays: Menthol-based lozenges or throat sprays can provide temporary relief by numbing the throat.
4. Warm Saltwater Gargle: Gargling with warm saltwater can help reduce inflammation and soothe a sore throat.
5. Humidification: Using a humidifier or inhaling steam from a bowl of hot water can add moisture to the air and soothe a dry, irritated throat.
6. Antibiotics (if necessary): Bacterial infections like strep throat may require antibiotics prescribed by a healthcare professional.
7. Avoiding Irritants: Avoiding smoking, secondhand smoke, and other environmental irritants can prevent further irritation to the throat.
When to See a Doctor:

throat pain
While most cases of throat pains resolve on their own or with home remedies, certain symptoms warrant medical attention:
– Persistent or severe throat pain that does not improve with self-care.
– Difficulty breathing or swallowing.
– High fever or persistent fever.
– Presence of white patches or pus on the throat.
– Swelling in the neck or difficulty opening the mouth.
Seeking prompt medical attention can help diagnose and treat underlying conditions, preventing complications and ensuring a speedy recovery.
Summary
An irritated or painful throat is called a sore throat. It usually feels worse after swallowing. A viral illness, like the flu or a cold, is the most frequent cause of pharyngitis, or sore throat.