Digestive health relevance. The creation of energy, the removal of waste, and the absorption of nutrients all depend on digestive health. Your immune system is strengthened, your mental health is enhanced, and many ailments are avoided when your digestive system is in good condition. On the other hand, chronic illnesses like irritable bowel syndrome or inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) as well as problems like malnourished and exhaustion can result from poor digestive health.
DIGESTIVE HEALTH RELEVANCE
The foundation of general health and wellbeing is digestive health. People may keep their digestive systems balanced and functioning well by learning about them, identifying frequent problems, and leading healthy lifestyles. In addition to improving digestion, putting gut health first also boosts immunity, mental well-being, and general quality of life.
The Digestive System: A Brief Overview;
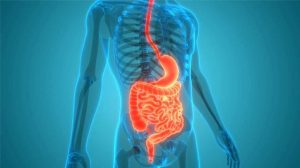
The digestive system includes the mouth, esophagus, stomach, intestines, liver, pancreas, and gallbladder. This system works cohesively to:
1. Break Down Food: Enzymes and stomach acids convert food into smaller molecules.
2. Absorb Nutrients: Nutrients pass through the intestinal walls into the bloodstream.
3. Eliminate Waste: Undigested food and waste products are excreted.
The Role of Gut Microbiota;
A crucial aspect of digestive health is the gut microbiota, the diverse community of microorganisms living in the intestines. These microbes aid in digestion, produce vitamins, and play a significant role in immune function. A balanced gut microbiome contributes to better digestion, enhanced immune responses, and improved mental health, while an imbalance can lead to digestive issues and other health problems.
Common Digestive Health Issues;
Several conditions can affect digestive health, including:
1. Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease: Characterized by chronic acid reflux, causing heartburn and potential damage to the esophagus.
2. Irritable Bowel Syndrome: A disorder causing abdominal pain, bloating, and changes in bowel habits.
3. Inflammatory Bowel Disease: Includes conditions like Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis, which cause chronic inflammation of the digestive tract.
4. Celiac Disease: An autoimmune disorder where ingestion of gluten leads to damage in the small intestine.
Maintaining Digestive Health;

Good digestive health can be maintained through lifestyle choices and dietary habits:
1. Balanced Diet:
Consuming a variety of foods rich in fiber, vitamins, and minerals supports healthy digestion. Fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins are essential.
2. Hydration:
Drinking plenty of water aids digestion by helping to dissolve fats and soluble fiber.
3. Regular Exercise:

Digestive health relevance.
Physical activity promotes regular bowel movements and reduces stress, which can impact digestion.
4. Probiotics and Prebiotics:
Probiotics (beneficial bacteria) and prebiotics (food for these bacteria) support a healthy gut microbiota. Yogurt, kefir, sauerkraut, and fiber-rich foods are good sources.
5. Mindful Eating:

Digestive health relevance.
Eating slowly, chewing thoroughly, and being mindful of food choices can prevent overeating and aid digestion.
6. Limiting Processed Foods:
Reducing intake of processed foods, high in fats and sugars, can prevent digestive discomfort and promote better gut health.
The Connection Between Gut Health and Overall Well-being;
Emerging research highlights the profound connection between gut health and other aspects of health:
1. Immune System:
Digestive health relevance.
Approximately 70% of the immune system resides in the gut. A healthy gut can fend off pathogens and reduce inflammation.
2. Mental Health:
The gut-brain axis links digestive health to mental well-being. Gut microbes produce neurotransmitters like serotonin, influencing mood and cognitive function.
3. Weight Management:
Gut bacteria affect how we digest food and store fat. A balanced microbiome can help maintain a healthy weight.
When to Seek Medical Advice;

Digestive health relevance.
While maintaining a healthy lifestyle can prevent many digestive issues, it is crucial to seek medical advice when experiencing persistent symptoms such as:
Summary
The foundation of general well-being is digestive health, which affects everything from immune system performance and mental health to food absorption. A complex network of organs, the digestive system—also known as the gut—breaks down food, absorbs nutrients, and eliminates waste.