
Tools for professional videos. You cannot afford to overlook the revolution in internet video marketing, since it is anticipated that by 2022, video traffic will make up 80% of all online consumer traffic. However, particularly for small firms, the numerous processes involved in creating, releasing, and evaluating videos as well as the reactions of viewers can be costly and time-consuming. The solution is to develop, implement, and evaluate your video marketing campaign using the best technologies available.
TOLS FOR PROFESSIONAL VIDEOS
Creating a professional video requires a combination of technical expertise, creativity, and the right tools. Here are some essential tools needed for making a professional video:

A high-quality camera is essential for capturing crisp, clear footage. Whether it’s a DSLR, mirrorless camera, or cinema camera, choose one that meets your needs in terms of resolution, frame rate, and low-light performance.
2. Lenses
Invest in a selection of lenses to achieve different focal lengths and perspectives. Wide-angle lenses are great for capturing expansive scenes, while telephoto lenses are ideal for close-ups and detail shots.
3. Tripod

A sturdy tripod is essential for keeping your camera stable and ensuring smooth, shake-free shots. Look for one with adjustable legs and a fluid head for precise positioning and panning.
4. Microphone
Good audio is just as important as good video quality. Invest in a high-quality microphone to capture clear, professional sound. Options include shotgun microphones for on-camera use, lavalier microphones for interviews, and boom microphones for capturing dialogue on set.
5. Lighting

Proper lighting can make or break a video. Invest in a lighting kit with adjustable lights, softboxes, and diffusers to control the intensity and direction of light. Consider using natural light or LED panels for a soft, flattering look.
6. Editing Software
Choose a professional video editing software like Adobe Premiere Pro, Final Cut Pro, or DaVinci Resolve to edit and enhance your footage. These programs offer a wide range of editing tools, effects, and color grading capabilities to bring your vision to life.
7. Computer

Tools for Professional Videos
A powerful computer with ample processing power and storage is essential for editing high-resolution video files. Make sure your computer meets the system requirements of your chosen editing software to ensure smooth performance.
8. External Hard Drive

Tools for Professional Videos
Invest in an external hard drive to store and backup your video files. This will not only free up space on your computer but also provide a safe and secure way to archive your footage.
9. Graphics and Animation Software
Depending on your project, you may need graphics and animation software to create titles, lower thirds, and visual effects. Adobe After Effects is a popular choice for motion graphics and compositing.
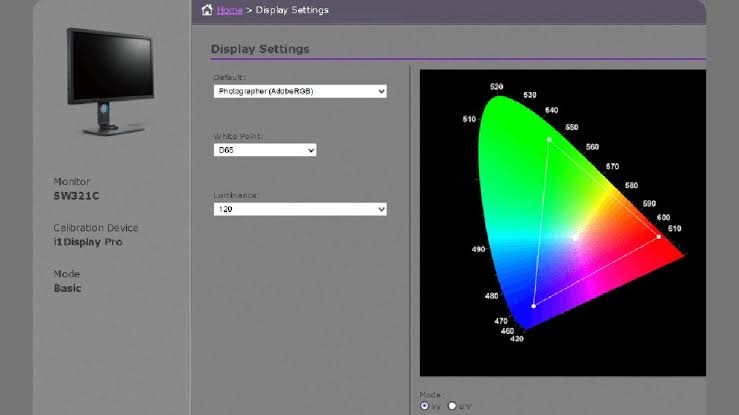
10. Color Calibration Tools

Tools for Professional Videos
Ensure color accuracy by using color calibration tools to calibrate your monitor and maintain consistent color throughout the editing process. This will help ensure that your video looks its best across different devices and platforms.
Summary
By investing in these essential tools and honing your skills, you’ll be well-equipped to create professional-quality videos that captivate and engage your audience.

Pingback: Is color calibration different from color grading? - SimplExplainer
Pingback: Understanding Techniques for Editing and Filming - SimplExplainer
Pingback: Colour Calibration and Grading Differences - SimplExplainer