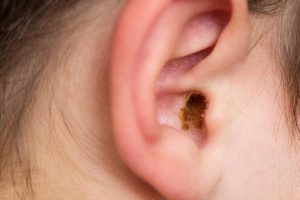
CAUSES OF EARWAX BLOCKAGE
Causes of earwax blockage. Hearing loss, discomfort, ear pain, lightheadedness, ringing in the ears, and other problems can result from untreated earwax accumulation. Earwax impaction is often not harmful, and with treatment, the symptoms disappear. Treatments for earwax blockages include manual removal at your doctor’s office or drops to loosen the wax.
CAUSES OF EARWAX BLOCKAGE
Earwax blockage is known medically as “cerumen impaction.” An essential component of ear health is earwax, or cerumen. In addition to cleaning your ears, it shields them from debris, dust, and infections. Even though earwax has many advantages, if too much of it accumulates, it can become problematic. Hearing loss, ringing in the ears, itching, and other problems can be caused by cerumen impaction. A medical professional can assist you in getting rid of earwax if needed.
Signs

Symptoms of impacted earwax can include:
a sensation of ear fullness.
Your ear is hurting (earache).
hearing loss that could get worse with time.
Tinnitus, or ringing in the ears.
You have itchy ears.
smell or discharge emanating from your ears.
Dizziness
Causes
Some persons get earwax buildup just because their earwax production is higher by nature.
Additionally, earwax impaction may occur if your earwax is firm or dry.
You have a lot of hair on your ears.
The canals in your ears are narrow.
You regularly wear hearing aids or earplugs.
You clean your ears on a regular basis with cotton swabs.
Treatment
Treatments for affected cerumen include both in-office and at-home techniques, such as earwax-dissolving solutions.
irrigation of the ears.
elimination of earwax in the workplace.
Consult your doctor before beginning any kind of treatment.
Be sure to thoroughly clean your ears by wiping the outside of your ears with a washcloth and drying them as much as you can after taking a bath or shower. Cotton swabs should never be used inside your ear canal because they can harm your eardrum and cause your ears to produce more earwax.
Watering the ears
Syringing or irrigating your ear is an additional choice. This entails cleaning your ear canal with water or saline solution using a syringe. Generally speaking, you should use a cerumenolytic solution to soften the wax first. After that, you will use a bulb syringe to gently irrigate your ear.
Removal of earwax in the workplace
Lastly, your healthcare practitioner may use specialized tools to manually remove earwax. They may employ irrigation, a suction device, forceps, or a cerumen spoon. These processes often just take a few minutes to finish.
Prevention

Avoid cleaning your ears with anything that sticks in them. Use cotton swabs just on the outside of your ear if you plan to use them. If your earwax removal is required more than once a year, ask your healthcare professional what they recommend to prevent earwax accumulation.
Summary
Recall that earwax by itself is not harmful. It prevents infections and cleanses your ears. Earwax accumulation, however, can result in problems including itching, discomfort, and hearing loss. Only cleaning the exterior of your ears and softening earwax with drops or water is safe. In order to remove earwax with an instrument, you should always get in touch with your healthcare professional.