Kale Nutritional value. More than just a popular superfood, kale is a nutrient-dense, adaptable vegetable that may greatly improve your diet. It is a beneficial addition to any meal because of its remarkable variety of vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants, which promote general health and wellbeing. Kale is a tasty method to increase your nutritional intake, whether it’s consumed raw, boiled, or mixed into smoothies.
KALE NUTRITIONAL VALUE
In recent years, kale has become increasingly popular and has gained a reputation as a nutritious powerhouse. This leafy green vegetable, which is a member of the Brassica family, is praised for its many health advantages and rich nutrient profile. Kale is a useful and adaptable complement to your meals, whether you want to increase your vitamin intake or diversify your diet.
Nutritional Profile;
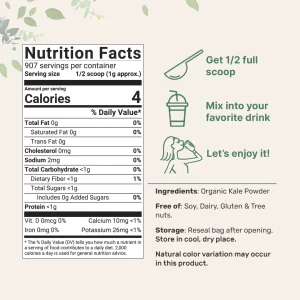
Kale is incredibly nutrient-dense, offering a wide array of vitamins and minerals in each serving:
– Vitamins: Kale is an excellent source of vitamins A, C, and K. Vitamin A supports vision and immune function. Vitamin C acts as a powerful antioxidant and boosts skin health, and vitamin K is crucial for blood clotting and bone health.
– Minerals: It provides significant amounts of calcium, potassium, and magnesium. All of which are essential for maintaining strong bones, muscle function, and cardiovascular health.
– Antioxidants: Kale is rich in antioxidants such as quercetin and kaempferol. This help protect the body from oxidative stress and inflammation.
– Fiber: High in dietary fiber, kale aids digestion, promotes a healthy gut, and can help lower cholesterol levels.
Health Benefits;

1. Improved Eye Health:
The high content of vitamin A and antioxidants like lutein and zeaxanthin in kale support good vision and can help prevent age-related eye conditions.
2. Strong Bones:
With substantial amounts of vitamin K and calcium, kale plays a crucial role in maintaining bone density and reducing the risk of osteoporosis.
3. Heart Health:

The fiber, potassium, and antioxidants in kale contribute to cardiovascular health by lowering blood pressure. Reducing cholesterol levels, and protecting against heart disease.
4. Anti-inflammatory Properties:
The antioxidants and omega-3 fatty acids in kales help reduce inflammation, which is linked to chronic diseases such as arthritis, diabetes, and heart disease.
5. Cancer Prevention:
Compounds in kales, like sulforaphane and indole-3-carbinol, have been shown to have anti-cancer properties, helping to protect against certain types of cancer.
Culinary Uses;

kale nutritional value
Kale’s versatility makes it easy to incorporate into various dishes:
– Salads:
Raw kales can be massaged with olive oil and lemon juice to soften its texture and reduce bitterness, making it a hearty base for salads.
– Smoothies:

kale nutritional value
Add a handful of kales to your morning smoothie for an extra nutrient boost without compromising on taste.
– Soups and Stews:
Kales can be added to soups, stews, and chilis, where it retains its texture and adds nutritional value.
– Sautéed or Steamed:
Sautéing or steaming kales with garlic and olive oil makes for a delicious and nutritious side dish.
– Chips:

kale nutritional value
Baked kale chips, seasoned with salt and spices, provide a healthy alternative to traditional snacks.
Summary
Like cabbage, broccoli, and cauliflower, kale is a cruciferous vegetable with big, edible leaves and a hard central stalk. Kale comes in a range of colors, including purple, though it is usually dark green. The leaves have either curled or flat margins. Kale can be eaten fresh or mildly cooked, and it is often sold whole or pre-chopped.

