
Causes of facial pain and management. Dental abscesses and tooth problems, temporomandibular joint difficulties, sinus infections, chronic headaches, and nerve conditions like shingles or trigeminal neuralgia can all cause facial pain. Seeing a doctor to determine the cause is part of management, which may include medicines for sinusitis and headaches, anticonvulsant drugs for nerve pain, or dental care for tooth pain. Certain types of facial discomfort can also be managed by changing one’s lifestyle, such as avoiding trigger foods and obtaining enough sleep.
CAUSES OF FACIAL PAIN AND MANAGEMENT
Facial pain can be a distressing symptom that affects various aspects of daily life, from eating and speaking to sleeping and socializingi. While facial pain can arise from a multitude of sources, understanding the common causes is crucial for effective management and relief. In this article, we’ll delve into the diverse causes of facial pain and discuss strategies for addressing this discomfort.
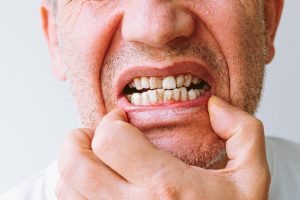
1. Dental Problems
CAUSES OF FACIAL PAIN AND MANAGEMENT
Dental issues are a leading cause of pain on the face, with conditions such as tooth decay, gum disease, and dental abscesses contributing to discomfort in the jaw, cheeks, and surrounding areas. Toothaches, jaw stiffness, and pain while chewing or biting are common symptoms of dental-related pain.
2. Sinus Infections
Sinus infections, also known as sinusitis, occur when the sinuses become inflamed and swollen due to infection or inflammation of the sinus tissues. Facial pain associated with sinusitis typically manifests as pressure or tenderness in the cheeks, forehead, and around the eyes. Other symptoms may include nasal congestion, headache, fatigue, and thick nasal discharge. Treatment for sinusitis may include antibiotics, nasal decongestants, saline nasal irrigation, and pain relief medication to alleviate symptoms and clear the infection.
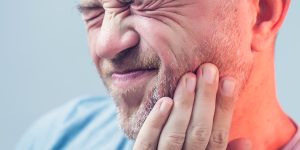
3. Temporomandibular Joint Disorders
CAUSES OF FACIAL PAIN AND MANAGEMENT
Temporomandibular joint disorders (TMJ disorders) affect the joints that connect the jawbone to the skull, leading to facial pain, jaw stiffness, and difficulty chewing or speaking. TMJ disorders can be caused by various factors, including jaw injury, teeth grinding (bruxism), arthritis, and stress. Treatment for TMJ disorders may include lifestyle modifications, dental appliances, physical therapy, stress management techniques, and in severe cases, surgery to repair or replace the affected joint.
4. Trigeminal Neuralgia
Trigeminal neuralgia is a chronic pain condition that affects the trigeminal nerve. Which is responsible for transmitting sensations from the face to the brain. Individuals with trigeminal neuralgia experience sudden, intense facial pain that can be triggered by activities such as eating, talking, or touching the face. The pain is often described as stabbing, shooting, or electric shock-like in nature and can be debilitating. Treatment for trigeminal neuralgia may include medications, nerve blocks, and surgical interventions to relieve pain and improve quality of life.
5. Facial Trauma
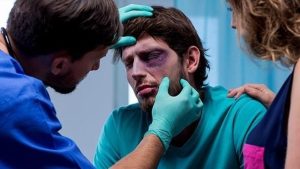
Facial trauma, such as fractures, bruises, or lacerations, can cause significant pain and discomfort in the affected area. Common causes of facial trauma include falls, motor vehicle accidents, sports injuries, and physical assaults. Depending on the severity of the injury, treatment may involve rest. Pain management, wound care, and in complex cases, surgical repair or reconstruction to restore facial function and appearance.
Summary
The pain can stem from a variety of sources, including dental problems, sinus infection. TMJ disorders, trigeminal neuralgia, and facial trauma. Identifying the underlying cause of facial pain is essential for implementing appropriate treatment and management strategies. If you experience persistent or severe pain on your face. It’s important to consult with a healthcare professional for proper evaluation and personalized care. With timely intervention and comprehensive management, individuals can find relief from facial pain and improve their overall quality of life.