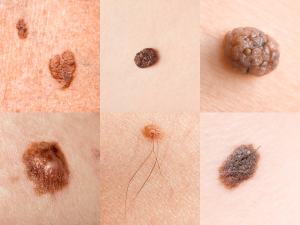
Signs of skin cancer. One kind of cancer that starts in skin cells is called skin cancer. Although it can happen in places that are not normally exposed to sunlight, it usually builds up in locations that have. Squamous cell carcinoma, basal cell carcinoma, and melanoma are among the various forms of skin cancer, each having unique traits and therapies. It’s crucial to routinely examine your skin for any odd changes and to see a doctor if you feel like you may have skin cancer.
SIGNS OF SKIN CANCER
Skin cancer is a dangerous and perhaps fatal condition. However, if caught early, it is also very treatable and preventative. by adopting sun-safe practices and being aware of any changes to the skin. Additionally, by promptly seeking medical assistance for worrisome lesions, people can lower their risk of developing skin cancer and increase their chances of long-term survival and successful treatment.
Common signs of skin cancer include:
– A new growth or sore that doesn’t heal
– Changes in the size, shape, color, or texture of existing moles or lesions
– Irregular borders or asymmetry of pigmented lesions
– Itching, tenderness, or pain in a mole or lesion
Preventive Measures:
1. Sun Protection:

Limit sun exposure, especially during peak hours (10 a.m. to 4 p.m.), and use sunscreen with a high SPF, protective clothing, hats, and sunglasses.
2. Regular Skin Exams:
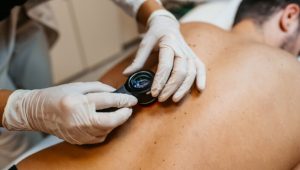
Perform self-exams of the skin to monitor for changes in moles or lesions, and schedule regular skin checks with a dermatologist.
3. Avoid Tanning Beds:
Avoid using tanning beds, as they emit harmful UV radiation that increases the risk of skin cancer.
4. Seek Shade:

When outdoors, seek shade under trees, umbrellas, or awnings to reduce direct sun exposure.
5. Protect Children:
Protect children from sun exposure by dressing them in protective clothing, applying sunscreen, and encouraging sun-safe behaviors.
6. Stay Hydrated:

Stay hydrated by drinking plenty of water, especially when spending time outdoors in the sun.
7. Be Sun Smart:
Be mindful of UV index forecasts and take appropriate precautions to protect your skin when UV levels are high.
8. Quit Smoking:

Smoking can increase the risk of developing certain types of skin cancer, so quitting smoking can lower your overall risk.
Early Detection and Treatment:
Early detection is key to successful treatment of skin cancer. Regular self-exams and annual skin checks by a dermatologist can help detect suspicious lesions or moles early, when treatment is most effective. If skin cancer is diagnosed, treatment options may include:
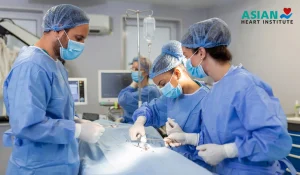
1. Surgery:
SIGNS OF SKIN CANCER
Surgical removal of the cancerous lesion or tumor is often the primary treatment for skin cancer. In some cases, Mohs surgery, a specialized surgical technique that removes thin layers of skin one at a time, may be recommended for certain types of skin cancer.
2. Radiation Therapy:
Radiation therapy may be used to destroy cancer cells or shrink tumors, particularly for cancers that are difficult to remove surgically or for patients who are not candidates for surgery.
3. Topical Treatments:

SIGNS OF SKIN CANCER
For superficial skin cancers or precancerous lesions, topical treatments such as topical chemotherapy, immunotherapy, or photodynamic therapy may be used to destroy abnormal cells.
4. Systemic Therapies:
In cases of advanced or metastatic skin cancer, systemic therapies such as targeted therapy, immunotherapy, or chemotherapy may be used to treat the cancer and manage symptoms.
5. Supportive Care:

SIGNS OF SKIN CANCER
Supportive care measures, such as pain management, wound care, and psychosocial support. Play an important role in helping patients cope with the physical and emotional challenges of skin cancer treatment.
Summary
Skin that doesn’t normally receive sunlight can develop several types of skin cancer. This probably indicates that these cancers are being caused by something else. Keep an eye out for any changes on your skin to lower your risk of developing these types of skin cancers. Inform your healthcare provider of these changes.


Pingback: Medical screenings for older people
Pingback: Elderly People Medical Checkup - SimplExplainer