How to treat skin cancer. Skin cancer, which is caused by abnormal skin cell proliferation, usually appears on sun-exposed skin. However, this prevalent type of cancer can also develop on parts of your skin that aren’t typically exposed to sunlight. When anything alters the way your skin cells grow, such as exposure to UV light, skin cancer develops.
HOW TO TREAT SKIN CANCER
Changes in the size, form, or color of skin growths, as well as the appearance of new lumps or patches, are symptoms. If detected early, the majority of skin cancers are curable. Radiation, chemotherapy, cryotherapy, and Mohs surgery are among the available treatments. If skin cancer is not detected early, it may spread to other parts of your body or to adjacent tissue. Thankfully, the majority of skin cancers are curable if detected and treated early. Therefore, if you suspect that you may have skin cancer, it’s critical to consult your doctor.
Types
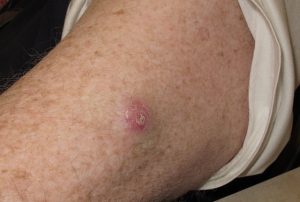
Basal cell carcinoma, which develops in the basal cells of the epidermis, the outermost layer of skin. • Squamous cell carcinoma, which develops in the outermost layer of your skin’s squamous cells. • Melanoma, which develops in melanocytes. The brown pigment known as melanin, which gives your skin its color and provides some protection from the sun’s harmful UV rays, is produced by melanocytes. Because it can spread to other parts of your body, this is the most dangerous kind of skin cancer.
Signs for Skin Cancer
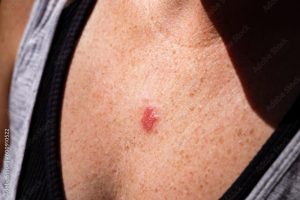
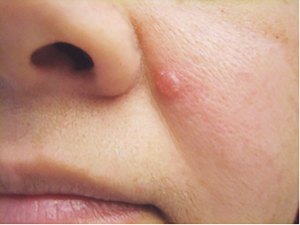
A change on your skin, either a new growth or a modification to an existing growth or mole, is the most prevalent warning sign of skin cancer. Symptoms of skin cancer include: • A fresh mole. or a mole that bleeds or varies in size, shape, or color. • A lump on your face, ears, or neck that is pearly or waxy. • A flat hump or patch that is pink, crimson, or brown in color. • Skin spots that appear to be scars. • Sores that bleed frequently, have a depression in the center, or appear crusty. • A sore or wound that either doesn’t heal or heals but recurs. • A scaly, rough lesion that may itch, bleed, and develop a crust.
Causes

Overexposure to sunlight is the primary cause of skin cancer, particularly when blistering and sunburned. The sun’s UV rays harm your skin’s DNA, which leads to the formation of aberrant cells. A mass of cancer cells is created when these aberrant cells divide quickly and haphazardly.
Treatment

The cancer’s stage determines the course of treatment. If the cancer is tiny and only affects the skin’s surface, a biopsy may be sufficient to remove all of the cancerous tissue. Other popular therapies for skin cancer, either by themselves or in combination, include: • Cryotherapy: To freeze skin cancer, your dermatologist employs liquid nitrogen. Following therapy, the dead cells slough off. • Excisional surgery: To ensure that all of the cancer has been removed, your dermatologist removes the tumor along with a portion of the surrounding good skin
More Treatment

HOW TO TREAT SKIN CANCER
Mohs surgery: Your dermatologist preserves as much of the surrounding healthy tissue as possible while removing only the problematic tissue. Basal cell and squamous cell cancers, as well as occasionally other skin cancers that appear close to delicate or aesthetically significant regions, such as your eyelids, ears, lips, forehead, scalp, fingers, or genital area, are treated by providers using this. • Radiation therapy: To either destroy cancer cells or prevent them from proliferating and dividing, your radiation oncologist employs radiation, which is a powerful beam of energy. • Photodynamic therapy: Using a blue or red fluorescent light, the dermatologist applies medication to your skin. Precancerous cells are destroyed by this treatment, but healthy cells remain unaffected.
Summary
Anyone can develop skin cancer. What could appear to be a harmless visual flaw might not actually be. Regular skin self-checks are essential for everyone. it’s particularly crucial if you are at a higher risk of developing skin cancer. The largest organ in your body is your skin. Additionally, it requires the same level of care as any other health issue. Every month, check your skin for any new growths or changes in existing spots.